Action Observation for Neurorehabilitation in Apraxia
- PMID: 31001194
- PMCID: PMC6456663
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00309
Action Observation for Neurorehabilitation in Apraxia
Abstract
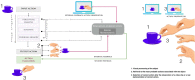
Neurorehabilitation and brain stimulation studies of post-stroke patients suggest that action-observation effects can lead to rapid improvements in the recovery of motor functions and long-term motor cortical reorganization. Apraxia is a clinically important disorder characterized by marked impairment in representing and performing skillful movements [gestures], which limits many daily activities and impedes independent functioning. Recent clinical research has revealed errors of visuo-motor integration in patients with apraxia. This paper presents a rehabilitative perspective focusing on the possibility of action observation as a therapeutic treatment for patients with apraxia. This perspective also outlines impacts on neurorehabilitation and brain repair following the reinforcement of the perceptual-motor coupling. To date, interventions based primarily on action observation in apraxia have not been undertaken.
Keywords: action execution; action recognition; apraxia; mirror activity; neurorehabilitation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The significance of clumsy gestures in apraxia following a left hemisphere stroke.Neuropsychol Rehabil. 2006 Feb;16(1):38-65. doi: 10.1080/09602010443000173. Neuropsychol Rehabil. 2006. PMID: 16509518
-
Action observation as a tool for neurorehabilitation to moderate motor deficits and aphasia following stroke.Neural Regen Res. 2012 Sep 15;7(26):2063-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.26.008. Neural Regen Res. 2012. PMID: 25624838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improving ideomotor limb apraxia by electrical stimulation of the left posterior parietal cortex.Brain. 2015 Feb;138(Pt 2):428-39. doi: 10.1093/brain/awu343. Epub 2014 Dec 5. Brain. 2015. PMID: 25481002
-
Distortion of Visuo-Motor Temporal Integration in Apraxia: Evidence From Delayed Visual Feedback Detection Tasks and Voxel-Based Lesion-Symptom Mapping.Front Neurol. 2018 Aug 27;9:709. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00709. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30210434 Free PMC article.
-
[How to diagnose and treat limb apraxia].Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2011 Jun;79(6):345-57. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1246097. Epub 2011 Apr 8. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2011. PMID: 21480158 Review. German.
Cited by
-
The Effectiveness of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Treating Apraxia.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024;23(8):1030-1039. doi: 10.2174/0118715273249412231010171926. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 37846576 Review.
-
The Role of Body in Brain Plasticity.Brain Sci. 2022 Feb 17;12(2):277. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12020277. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35204040 Free PMC article.
-
A Therapeutic Matrix: Virtual Reality as a Clinical Tool for Spinal Cord Injury-Induced Neuropathic Pain.Brain Sci. 2021 Sep 12;11(9):1201. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11091201. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 34573221 Free PMC article.
-
Apraxia Rehabilitation Using Gesture Training and Sequencing Tasks: A Case Report.Cureus. 2025 Jan 7;17(1):e77115. doi: 10.7759/cureus.77115. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 39925578 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Upper Limb Apraxia on General and Domain-Specific Self-Efficacy in Post-Stroke Patients.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Aug 10;11(16):2252. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11162252. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37628450 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

