NF-κB Signaling and IL-4 Signaling Regulate SATB1 Expression via Alternative Promoter Usage During Th2 Differentiation
- PMID: 31001272
- PMCID: PMC6454056
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00667
NF-κB Signaling and IL-4 Signaling Regulate SATB1 Expression via Alternative Promoter Usage During Th2 Differentiation
Abstract
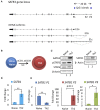
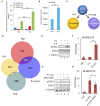
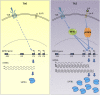
SATB1 is a genome organizer protein that is expressed in a lineage specific manner in CD4+ T-cells. SATB1 plays a crucial role in expression of multiple genes throughout the thymic development and peripheral differentiation of T cells. Although SATB1 function has been subjected to intense investigation, regulation of SATB1 gene expression remains poorly understood. Analysis of RNA-seq data revealed multiple transcription start sites at the upstream regulatory region of SATB1. We further demonstrated that SATB1 gene is expressed via alternative promoters during T-helper (Th) cell differentiation. The proximal promoter "P1" is used more by the naïve and activated CD4+ T-cells whereas the middle "P2" and the distal "P3" promoters are used at a significantly higher level by polarized T-helper cells. Cytokine and TCR signaling play crucial roles toward SATB1 alternative promoter usage. Under Th2 polarization conditions, transcription factor STAT6, which operates downstream of the cytokine signaling binds to the P2 and P3 promoters. Genetic perturbation by knockout and chemical inhibition of STAT6 activation resulted in the loss of P2 and P3 promoter activity. Moreover, chemical inhibition of activation of NF-κB, a transcription factor that operates downstream of the TCR signaling, also resulted in reduced P2 and P3 promoter usage. Furthermore, usage of the P1 promoter correlated with lower SATB1 protein expression whereas P2 and P3 promoter usage correlated with higher SATB1 protein expression. Thus, the promoter switch might play a crucial role in fine-tuning of SATB1 protein expression in a cell type specific manner.
Keywords: SATB1; STAT6; TCR signaling; alternative promoter; cytokine signaling.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dynamic regulation of chromatin organizer SATB1 via TCR-induced alternative promoter switch during T-cell development.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jun 19;48(11):5873-5890. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa321. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32392347 Free PMC article.
-
Autocrine IL-4 gene regulation at late phases of TCR activation in differentiated Th2 cells.J Immunol. 2002 Sep 15;169(6):3030-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.6.3030. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12218118
-
Stat6 inhibits human interleukin-4 promoter activity in T cells.Blood. 1998 Dec 15;92(12):4529-38. Blood. 1998. PMID: 9845517
-
Differential requirements for IL-4/STAT6 signalling in CD4 T-cell fate determination and Th2-immune effector responses.Immunol Cell Biol. 2010 Mar-Apr;88(3):240-3. doi: 10.1038/icb.2009.101. Epub 2009 Dec 15. Immunol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20010912 Review.
-
STAT6-dependent and -independent mechanisms in Th2 polarization.Eur J Immunol. 2012 Nov;42(11):2827-33. doi: 10.1002/eji.201242433. Epub 2012 Oct 8. Eur J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23041833 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic regulation of chromatin organizer SATB1 via TCR-induced alternative promoter switch during T-cell development.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jun 19;48(11):5873-5890. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa321. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 32392347 Free PMC article.
-
A dual function for the chromatin organizer Special A-T rich Binding Protein 1 in B-lineage cells.Cell Mol Immunol. 2023 Oct;20(10):1114-1126. doi: 10.1038/s41423-023-01069-y. Epub 2023 Aug 7. Cell Mol Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37544964 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation and Regulation of Bovine Th2 Cells In Vitro.Cells. 2024 Apr 24;13(9):738. doi: 10.3390/cells13090738. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38727273 Free PMC article.
-
A novel SATB1 protein isoform with different biophysical properties.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Aug 11;11:1242481. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1242481. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37635874 Free PMC article.
-
SATB1 in cancer progression and metastasis: mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 25;15:1535929. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1535929. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40071088 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

