Comparison of the Efficacy between Conventional Moxibustion and Smoke-Free Moxibustion on Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 31001350
- PMCID: PMC6437731
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/1291947
Comparison of the Efficacy between Conventional Moxibustion and Smoke-Free Moxibustion on Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the difference of efficacy between conventional moxibustion (CM) and smoke-free moxibustion (SM) for patients with osteoarthritis of the knee (KOA).
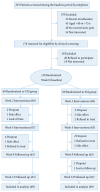
Methods: This is a multicentre, randomized, single blinded, parallel-group clinical trial. Patients with KOA were randomly allocated to CM group (69) and SM group (69) in 7 hospitals of China. Moxibustion treatment in 12 sessions over 4 weeks was administrated at 3 acupuncture points (EX-LE4, ST35, and ST36). Patients completed standard questionnaires at baseline and after 2 weeks, 4 weeks, 8 weeks, and 12 weeks. The primary outcome was the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) from the baseline to 4 weeks. The secondary outcomes include Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and Patient Global Assessment score (PGA).
Results: Analyses showed that the WOMAC score improved in pain (95% CI,-0.1[-1.2 to 0.9], p=0.76), stiffness (95% CI,-0.1 [-0.5 to 0.3], p=0.71), and function (95% CI, 2.2 [-1.3 to 5.8], p=0.22) compared between the two groups at 4 weeks, as well as the VAS score (95% CI,0.1 [-0.3 to 0.6], p=0.60). Similar results presented at 8 and 12 weeks. No statistically significant difference was observed between CM and SM groups for outcome measurements.
Conclusions: It suggested that smoke generated during moxibustion treatment does not affect the efficacy of moxibustion in the treatment of KOA, which should be taken into account to be removed for the sake of reducing environmental pollution or moxa smoke exposure of acupuncturists or patients. This trial is registered with Clinical Trials.gov, NCT02772055.
Figures
References
-
- Hay E. M., Foster N. E., Thomas E., et al. Effectiveness of community physiotherapy and enhanced pharmacy review for knee pain in people aged over 55 presenting to primary care: pragmatic randomised trial. British Medical Journal. 2006;333(7576):995–998. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38977.590752.0B. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical