In Vitro Antiatherothrombotic Effects of Extracts from Berberis Vulgaris L., Teucrium Polium L., and Orthosiphon Stamineus Benth
- PMID: 31001352
- PMCID: PMC6437728
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/3245836
In Vitro Antiatherothrombotic Effects of Extracts from Berberis Vulgaris L., Teucrium Polium L., and Orthosiphon Stamineus Benth
Abstract
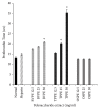
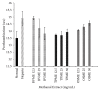
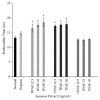
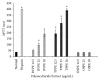
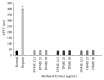
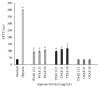
Coronary artery disease is the leading cause of mortality and morbidity worldwide. The pathogenesis is mainly due to atherosclerosis, plaque rupture, and platelet thrombus formation. The main risk factors for coronary artery disease include obesity, hypercholesterolemia, smoking, diabetes, and high blood pressure. As a part of disease management, treatment options using anticoagulant and antiplatelet drugs can be applied with addition to lipid-lowering medication. However, medicinal plants comprising antiatherothrombotic effects can be used as options to combat the disease rather than drug therapies with lesser adverse effects. Therefore, the haematological effect of Berberis vulgaris L., Teucrium polium L., and Orthosiphon stamineus Benth extracts was studied using in vitro model to prevent and to treat coronary atherothrombotic disease. The aqueous, methanol, and polysaccharide extracts of B. vulgaris, T. polium, and O. stamineus, respectively, were studied for their anticoagulant and antiplatelet effect on human whole blood. Extracts were subjected to the prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) test for anticoagulant activity. The antiplatelet activity was investigated using an electrical impedance method. B. vulgaris aqueous extract (BVAE), B. vulgaris polysaccharide extract (BVPE), T. polium aqueous extract (TPAE), and T. polium polysaccharide extract (TPPE) significantly prolonged the coagulation time in a concentration-dependent manner (p<0.05). The administration of BVAE demonstrated the most effective antiplatelet activity against platelet aggregation caused by arachidonic acid (AA) and collagen. These antiplatelet activities may correspond to the presence of higher total phenolic compound, which thus inhibit the platelet aggregation activity. In conclusion, these findings provide strong evidence on the antiatherothrombotic effect of BVAE and TPAE.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization W., Federation W. H., Organization W. S. W. W. H. F. W. S. Organization. Global Atlas on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Control. 2011. (W. W. H. F. W. S. Organization (Series Ed.)).
-
- Johnell M., Elgue G., Larsson R., Larsson A., Thelin S., Siegbahn A. Coagulation, fibrinolysis, and cell activation in patients and shed mediastinal blood during coronary artery bypass grafting with a new heparin-coated surface. The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. 2002;124(2):321–332. doi: 10.1067/mtc.2002.122551. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

