Pharmacological Prevention of Postoperative Delirium: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 31001357
- PMCID: PMC6437723
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/9607129
Pharmacological Prevention of Postoperative Delirium: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
Background: The high prevalence of delirium among postoperative patients has increased morbidity and mortality. The kind of drug that can effectively reduce the incidence of delirium has become the focus of discussion in recent years. However, a consensus in this respect has yet to be reached.
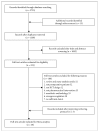
Methods: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were retrieved from the PubMed, Cochrane Library, ClinicalTrials.gov, and Embase databases from their inception through October 12, 2018. We included RCTs of pharmacological prevention for postoperative delirium in adults (at least 18 years), and the Cochrane risk of bias tool was used to evaluate the methodological quality of trials. The primary outcomes were the risk ratios (RRs) of incidence of postoperative delirium, and the secondary outcomes were the RRs of mortality and adverse events in the intervention and control groups.
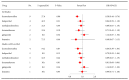
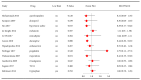
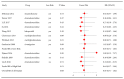
Results: Thirty-eight trials, which comprised 20302 patients and 18 different drugs, were included in the analysis. Of the 38 studies, 17 were rated as low risk with respect to methodological quality. Dexmedetomidine administration (RR 0.58, 95%CI 0.44-0.76, P<0.01) was associated with a significantly lower incidence of postoperative delirium than the control conditions. However, the findings from the studies with a low risk of bias did not show a significant difference in this beneficial effect (RR 0.64, 95%CI 0.39-1.04, P=0.07). The antipsychotic drugs olanzapine (RR 0.44, 95%CI 0.30- 0.65, P<0.01) and risperidone (RR 0.42, 95%CI 0.19-0.92, P=0.03) had promising effects, but there was a lack of sufficient evidence to obtain a definitive conclusion. The beneficial effect of other drugs, including haloperidol, methylprednisolone, dexamethasone, gabapentin, ketamine, cyproheptadine, donepezil, hypertonic saline, melatonin, nimodipine, ondansetron, pregabalin, rivastigmine, TJ-54, and tryptophan, was not proven on the basis of present evidence.
Conclusion: Among the pharmacological prophylactic measures for postoperative delirium, dexmedetomidine, olanzapine, and risperidone showed higher efficacy than other drugs. However, more high-quality evidence is needed to confirm these results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effectiveness and harms of pharmacological interventions for the treatment of delirium in adults in intensive care units after cardiac surgery: a systematic review.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2019 Oct;17(10):2020-2074. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-D-18-00010. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2019. PMID: 31449136
-
Association of Delirium Response and Safety of Pharmacological Interventions for the Management and Prevention of Delirium: A Network Meta-analysis.JAMA Psychiatry. 2019 May 1;76(5):526-535. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.4365. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30810723 Free PMC article.
-
Perioperative dexmedetomidine reduces delirium in elderly patients after non-cardiac surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials.Can J Anaesth. 2019 Dec;66(12):1489-1500. doi: 10.1007/s12630-019-01440-6. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Can J Anaesth. 2019. PMID: 31264195 English.
-
Dexmedetomidine in prevention and treatment of postoperative and intensive care unit delirium: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Intensive Care. 2018 Sep 20;8(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s13613-018-0437-z. Ann Intensive Care. 2018. PMID: 30238227 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of haloperidol for delirium prevention in adult patients: An updated meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Clin Anesth. 2020 May;61:109623. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2019.09.017. Epub 2019 Oct 28. J Clin Anesth. 2020. PMID: 31672417 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and validation of delirium prediction model for critically ill adults parameterized to ICU admission acuity.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 19;15(8):e0237639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237639. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32813717 Free PMC article.
-
Music to prevent deliriUm during neuroSurgerY (MUSYC) Clinical trial: a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.BMJ Open. 2021 Oct 1;11(10):e048270. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-048270. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 34598983 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological strategies to prevent postoperative delirium: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2021 Jan;16(1):28-48. doi: 10.17085/apm.20079. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Anesth Pain Med (Seoul). 2021. PMID: 33445233 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of dexmedetomidine on postoperative delirium and early postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients undergoing hepatic lobectomy.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Feb 28;47(2):219-225. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2022.210280. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 35545412 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Chinese, English.
-
Circulatory effects of dexmedetomidine in early sepsis: a randomised controlled experimental study.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020 Jan;393(1):89-97. doi: 10.1007/s00210-019-01713-3. Epub 2019 Aug 17. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31422445
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

