Design and Workspace Analysis of a Parallel Ankle Rehabilitation Robot (PARR)
- PMID: 31001407
- PMCID: PMC6437750
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/4164790
Design and Workspace Analysis of a Parallel Ankle Rehabilitation Robot (PARR)
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Design and Workspace Analysis of a Parallel Ankle Rehabilitation Robot (PARR).J Healthc Eng. 2021 Jan 28;2021:7345780. doi: 10.1155/2021/7345780. eCollection 2021. J Healthc Eng. 2021. PMID: 33564389 Free PMC article.
Abstract
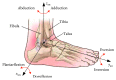
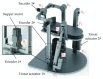
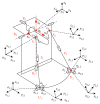
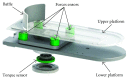
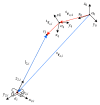
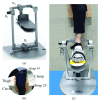
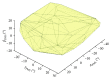
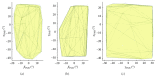
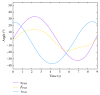
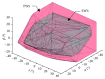
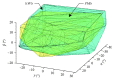
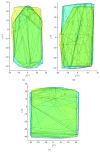
The ankle rehabilitation robot is essential equipment for patients with foot drop and talipes valgus to make up deficiencies of the manual rehabilitation training and reduce the workload of rehabilitation physicians. A parallel ankle rehabilitation robot (PARR) was developed which had three rotational degrees of freedom around a virtual stationary center for the ankle joint. The center of the ankle should be coincided with the virtual stationary center during the rehabilitation process. Meanwhile, a complete information acquisition system was constructed to improve the human-machine interactivity among the robot, patients, and physicians. The physiological motion space (PMS) of ankle joint in the autonomous and boundary elliptical movements was obtained with the help of the RRR branch and absolute encoders. The natural extreme postures of the ankle complex are the superposition of the three typical movements at the boundary motions. Based on the kinematic model of PARR, the theoretical workspace (TWS) of the parallel mechanism was acquired using the limit boundary searching method and could encircle PMS completely. However, the effective workspace (EWS) was smaller than TWS due to the physical structure, volume, and interference of mechanical elements. In addition, EWS has more clinical significance for the ankle rehabilitation. The PARR prototype satisfies all single-axis rehabilitations of the ankle and can cover most compound motions of the ankle. The goodness of fit of PMS can reach 93.5%. Hence, the developed PARR can be applied to the ankle rehabilitation widely.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A multi-degree-of-freedom reconfigurable ankle rehabilitation robot with adjustable workspace for post-stroke lower limb ankle rehabilitation.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Nov 24;11:1323645. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1323645. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38076434 Free PMC article.
-
State of the art in parallel ankle rehabilitation robot: a systematic review.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2021 Mar 20;18(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12984-021-00845-z. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2021. PMID: 33743757 Free PMC article.
-
Towards Optimal Platform-Based Robot Design for Ankle Rehabilitation: The State of the Art and Future Prospects.J Healthc Eng. 2018 Mar 15;2018:1534247. doi: 10.1155/2018/1534247. eCollection 2018. J Healthc Eng. 2018. PMID: 29736230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design and Experimental Research of 3-RRS Parallel Ankle Rehabilitation Robot.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Jun 16;13(6):950. doi: 10.3390/mi13060950. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35744564 Free PMC article.
-
A spherical parallel three degrees-of-freedom robot for ankle-foot neuro-rehabilitation.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012;2012:3356-9. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2012.6346684. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012. PMID: 23366645
Cited by
-
A multi-degree-of-freedom reconfigurable ankle rehabilitation robot with adjustable workspace for post-stroke lower limb ankle rehabilitation.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Nov 24;11:1323645. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1323645. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38076434 Free PMC article.
-
Retracted: Design and Workspace Analysis of a Parallel Ankle Rehabilitation Robot (PARR).J Healthc Eng. 2021 Jan 28;2021:7345780. doi: 10.1155/2021/7345780. eCollection 2021. J Healthc Eng. 2021. PMID: 33564389 Free PMC article.
-
Kinematic Calibration of a Parallel 2-UPS/RRR Ankle Rehabilitation Robot.J Healthc Eng. 2020 Sep 3;2020:3053629. doi: 10.1155/2020/3053629. eCollection 2020. J Healthc Eng. 2020. PMID: 32963748 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing healthcare through mobile collaboration: a survey of intelligent nursing robots research.Front Public Health. 2024 Nov 26;12:1368805. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1368805. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39659720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
State of the art in parallel ankle rehabilitation robot: a systematic review.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2021 Mar 20;18(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12984-021-00845-z. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2021. PMID: 33743757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jamwal P. K., Hussain S., Ghayesh M. H., Rogozina S. V. Adaptive impedance control of parallel ankle rehabilitation robot. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control . 2017;139(11) doi: 10.1115/1.4036560.111006 - DOI
-
- Girone M., Burdea G., Bouzit M. “Rutgers Ankle” orthopedic rehabilitation interface. Proceedings of the Asme Dynamic Systems and Control Division . 1999;67:305–312.
-
- Dai J. S., Zhao T., Nester C. Sprained ankle physiotherapy based mechanism synthesis and stiffness analysis of a robotic rehabilitation device. Autonomous Robots . 2004;16(2):207–218. doi: 10.1023/b:auro.0000016866.80026.d7. - DOI
-
- Liu G., Gao J., Yue H., Zhang X., Lu G. Design and kinematics simulation of parallel robots for ankle rehabilitation. Proceedings of IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems; October 2006; Beijing, China. pp. 253–258.
-
- Saglia J. A., Tsagarakis N. G., Dai J. S., Caldwell D. G. A high-performance redundantly actuated parallel mechanism for ankle rehabilitation. International Journal of Robotics Research . 2009;28(9):1216–1227. doi: 10.1177/0278364909104221. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

