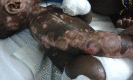
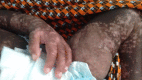
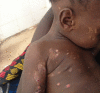
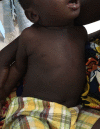
Bullous dermatosis suspected in an 8-month-old child in Guinea-Bissau
- PMID: 31001428
- PMCID: PMC6464016
- DOI: 10.1093/omcr/omz004
Bullous dermatosis suspected in an 8-month-old child in Guinea-Bissau
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: Bullous dermatosis suspected in an eight-month-old child in Guinea-Bissau: a case report.Oxf Med Case Reports. 2021 Feb 15;2021(2):omaa139. doi: 10.1093/omcr/omaa139. eCollection 2021 Feb. Oxf Med Case Reports. 2021. PMID: 33614049 Free PMC article.
Abstract
An 8-month-old child was admitted to a paediatric intensive care unit in Guinea-Bissau with severe blistering dermatosis. He was treated with broad spectrum antibiotics and dressings, without improvement. After 2 weeks, linear IgA bullous dermatosis was suspected. Owing to lack of dapsone, the child was treated with prednisolone and improved. To avoid corticosteroids side effects, 2 months after starting prednisolone we switched to colchicine, but the boy's condition worsened for reasons of poor adherence, requiring intravenous corticosteroids and antibiotics. After complete resolution of the skin lesions, we continued with colchicine monotherapy, then changed to dapsone after 3 months. The child did not show any further signs of dermatosis, but his follow-up ended abruptly, because he did not return to the hospital. IgA bullous dermatosis is a challenging diagnosis in settings where pathological studies cannot be conducted. Multidisciplinary treatment is required and colchicine is a good option if dapsone is not available.
Figures
References
-
- Wojnarowska F, Marsden RA, Bhogal B, Black MM. Chronic bullous disease of childhood, childhood cicatricial pemphigoid, and linear IgA disease of adults. J Am Acad Dermatol 1988;19:792–805. - PubMed
-
- Kharfi M, Khaled A, Karaa A, Zaraa I, Fazaa B, Kamou MR. Linear IgA bullous dermatosis: the more frequent bullous dermatosis of children. Dermatol Online J 2010;16:2. - PubMed
-
- Venning VA Linear IgA disease: clinical presentation, diagnosis, and pathogenesis. Dermatol Clin 2011;29:453–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous