A Predictive Model of Postnatal Surgical Intervention in Children With Prenatally Detected Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract
- PMID: 31001505
- PMCID: PMC6454042
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2019.00120
A Predictive Model of Postnatal Surgical Intervention in Children With Prenatally Detected Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract
Abstract
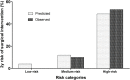
The aim of this study was to identify predictive factors and develop a model to assess individualized risk of postnatal surgical intervention in patients with antenatal hydronephrosis. This is a retrospective cohort study of 694 infants with prenatally detected congenital anomalies of kidney and urinary tract with a median follow-up time of 37 months. The main event of interest was postnatal surgical intervention. A predictive model was developed using Cox model with internal validation by bootstrap technique. Of 694 patients, 164 (24%) infants underwent surgical intervention in a median age of 7.8 months. Predictors of the surgical intervention in the model were: baseline glomerular filtration rate, associated hydronephrosis, presence of renal damage and the severity of renal pelvic dilatation. The optimism corrected c statistic for the model was 0.84 (95%CI, 0.82-0.87). The predictive model may contribute to identify infants at high risk for surgical intervention. Further studies are necessary to validate the model in patients from other settings.
Keywords: antenatal hydronephrosis; congenital anomalies of kidney and urinary tract; predictive model; prenatal diagnosis; surgical intervention.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Outcome after prenatal diagnosis of congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract.Eur J Pediatr. 2016 May;175(5):667-76. doi: 10.1007/s00431-015-2687-1. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Eur J Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 26805407
-
The Diagnostic Efficacy of and Requirement for Postnatal Ultrasonography Screening for Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Sep 30;13(19):3106. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13193106. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835849 Free PMC article.
-
A predictive model of chronic kidney disease in patients with congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract.Pediatr Nephrol. 2014 Dec;29(12):2357-64. doi: 10.1007/s00467-014-2870-z. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Pediatr Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24942863
-
[Postnatal management of urinary tract anomalies after antenatal diagnosis].J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2003 Jun;32(4):300-13. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2003. PMID: 12843878 Review. French.
-
Urinary biomarkers in hydronephrosis.Dan Med J. 2013 Feb;60(2):B4582. Dan Med J. 2013. PMID: 23461995 Review.
Cited by
-
How combining different caries lesions characteristics may be helpful in short-term caries progression prediction: model development on occlusal surfaces of primary teeth.BMC Oral Health. 2021 May 12;21(1):255. doi: 10.1186/s12903-021-01568-2. BMC Oral Health. 2021. PMID: 33980210 Free PMC article.
-
Renal function in pediatric urologic surgical patients: Insight from the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program-Pediatric cohort.Curr Urol. 2025 May;19(3):224-229. doi: 10.1097/CU9.0000000000000234. Epub 2024 Mar 12. Curr Urol. 2025. PMID: 40376472 Free PMC article.
-
Congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract: defining risk factors of disease progression and determinants of outcomes.Pediatr Nephrol. 2023 Dec;38(12):3963-3973. doi: 10.1007/s00467-023-05899-w. Epub 2023 Mar 3. Pediatr Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36867265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-surgical management of vesicoureteral junction obstruction: a case report.J Bras Nefrol. 2022 Apr-Jun;44(2):296-300. doi: 10.1590/2175-8239-JBN-2020-0152. J Bras Nefrol. 2022. PMID: 33605312 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and Clinical Factors Influencing Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract in Children: Insights from Prenatal and Postnatal Assessments.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 8;12(8):1798. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081798. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200262 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

