The Complex Etiology of Childhood Obesity in Arabs Is Highlighted by a Combination of Biological and Socio-Economic Factors
- PMID: 31001508
- PMCID: PMC6455072
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2019.00072
The Complex Etiology of Childhood Obesity in Arabs Is Highlighted by a Combination of Biological and Socio-Economic Factors
Abstract
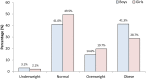
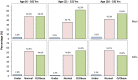
Objectives: To identify predictors of childhood and adolescent obesity in Kuwaitis with Arab ethnicity. Methods: A cross-sectional sample of 6-18 year-old schoolchildren was randomly selected from 244 public schools across all six governorates in the State of Kuwait. Anthropometric data were measured from 6,574 Arab Kuwaiti schoolchildren, and a structured questionnaire was used to collect information on possible risk factors associated with obesity. Overweight and obesity were defined in accordance with the Center for Disease Control and Prevention criteria. Results: The prevalence of overweight and obesity in children (aged 6-18 years) were 17.7% and 33.7%, respectively. The likelihood of childhood obesity increased with birth weights >4.0 Kg [odds ratio (OR) = 2.3; p < 0.0001], maternal employment (OR = 1.26, p = 0.0006), maternal age at pregnancy >30 years (OR = 1.24; p = 0.0016) and family size of <6 members (OR = 1.16, p = 0.0106). Conclusions: Public health professionals should be aware that advanced maternal age, maternal employment, smaller family size, and high birthweight may predict the risk of obesity in Kuwaiti Arab children and adolescents.
Keywords: Arabs; children; obesity; prevalence; risk factors.
Figures
References
-
- Sinaiko AR, Jacobs DR, Jr, Steinberger J, Moran A, Luepker R, Rocchini AP, et al. Prineas, insulin resistance syndrome in childhood: associations of the euglycemic insulin clamp and fasting insulin with fatness and other risk factors. J Pediatr. (2001) 139:700–7. 10.1067/mpd.2001.118535 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

