Atmospheric Aerosol Assisted Pulsed Plasma Polymerization: An Environmentally Friendly Technique for Tunable Catechol-Bearing Thin Films
- PMID: 31001513
- PMCID: PMC6454202
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00183
Atmospheric Aerosol Assisted Pulsed Plasma Polymerization: An Environmentally Friendly Technique for Tunable Catechol-Bearing Thin Films
Abstract
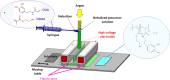
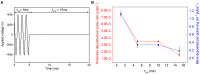
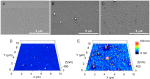
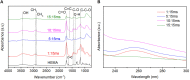
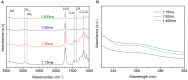
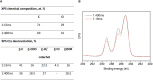
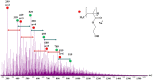
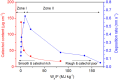
In this work, an atmospheric aerosol assisted pulsed plasma process is reported as an environmentally friendly technique for the preparation of tunable catechol-bearing thin films under solvent and catalyst free conditions. The approach relies on the direct injection of dopamine acrylamide dissolved in 2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate as comonomer into the plasma zone. By adjusting the pulsing of the electrical discharge, the reactive plasma process can be alternatively switch ON (tON) and OFF (tOFF) during different periods of time, thus allowing a facile and fine tuning of the catechol density, morphology and deposition rate of the coating. An optimal tON/tOFF ratio is established, that permits maximizing the catechol content in the deposited film. Finally, a diagram, based on the average energy input into the process, is proposed allowing for easy custom synthesis of layers with specific chemical and physical properties, thus highlighting the utility of the developed dry plasma route.
Keywords: coating; dry process; plasma polymerization; surface modification; tunable catechol films.
Figures
References
-
- Beamson G., Briggs D. (1992). High Resolution XPS of Organic Polymers: The Scienta ESCA 300 database. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons.
-
- Borris J., Thomas M., Klages C. –P., Faupel F., Zaporojtchenko V. (2007). Investigations into composition and structure of DBD-deposited amino group containing polymer layers. Plasma Process. Polym. 4, S482–486. 10.1002/ppap.200731211 - DOI
-
- Camporeale G., Moreno-Couranjou M., Bonot S., Mauchauff,é R., Boscher N. D., Bebrone C., et al. (2015). Atmospheric-pressure plasma deposited epoxy-rich thin films as platforms for biomolecule immobilization—application for anti-biofouling and xenobiotic-degrading surfaces. Plasma Process. Polym. 12, 1208–1219. 10.1002/ppap.201400206 - DOI
-
- Chen W.-Y., Matthews A., Jones F. R., Chen K.-S. (2018). Deposition of a stable and high concentration of carboxylic acid functional groups onto a silicon surface via a tailored remote atmospheric pressure plasma process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 336, 67–71. 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.09.057 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

