Fibronectin Functionalized Electrospun Fibers by Using Benign Solvents: Best Way to Achieve Effective Functionalization
- PMID: 31001528
- PMCID: PMC6456675
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00068
Fibronectin Functionalized Electrospun Fibers by Using Benign Solvents: Best Way to Achieve Effective Functionalization
Abstract
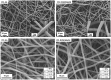
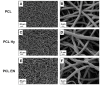
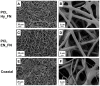
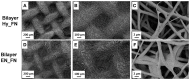
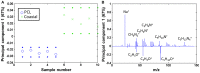
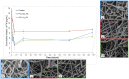
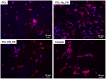
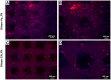
The aim of this study is to demonstrate the feasibility of different functionalization methods for electrospun fibers developed using benign solvents. In particular three different approaches were investigated to achieve the functionalization of poly(epsilon caprolactone) (PCL) electrospun fibers with fibronectin. Protein surface entrapment, chemical functionalization and coaxial electrospinning were performed and compared. Moreover, bilayered scaffolds, with a top patterned and functionalized layer with fibronectin and a randomly oriented not functionalized layer were fabricated, demonstrating the versatility of the use of benign solvents for electrospinning also for the fabrication of complex graded structures. Besides the characterization of the morphology of the obtained scaffolds, ATR-FTIR and ToF-SIMS were used for the surface characterization of the functionalized fibers. Cell adhesion and proliferation were also investigated by using ST-2 cells. Positive results were obtained from all functionalized scaffolds and the most promising results were obtained with bilayered scaffolds, in terms of cells infiltration inside the fibrous structure.
Keywords: benign solvents; electrospinning; fibronectin; functionalization; nanofibers; scaffolds; tissue engineering.
Figures




References
-
- Chakrapani V. Y., Gnanamani A., Giridev V. R., Madhusoothanan M., Sekaran G. (2012). Electrospinning of type I collagen and PCL nanofibers using acetic acid. J. Appl. Polymer Sci. 125, 3221–3227. 10.1002/app.36504 - DOI
-
- Chutipakdeevong J., Ruktanonchai U., Supaphol P. (2014). Hybrid biomimetic electrospun fibrous mats derived from poly(ε-caprolactone) and silk fibroin protein for wound dressing application. J. Appl. Polymer Sci. 132:41653 10.1002/app.41653 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

