Therapeutic Challenges in Management of Severe Acidosis and Profound Hypokalemia in Pediatric Diabetic Ketoacidosis
- PMID: 31001573
- PMCID: PMC6454640
- DOI: 10.1177/2333794X19840364
Therapeutic Challenges in Management of Severe Acidosis and Profound Hypokalemia in Pediatric Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Abstract
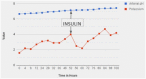
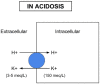
Profound hypokalemia in the presence of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is life-threatening condition predisposing patients to cardiac arrhythmias and potentially death. Rarely do patients present with profound hypokalemia (serum K+ level <2.5 mEq/L). Pediatric patients who present to the hospital with new-onset DKA with no past medical history and have profound severe hypokalemia and acidosis can be very difficult to manage. Given insulin to these patients immediately can lead to further decrease in extracellular potassium level and lead to cardiac dysrhythmias and death. We present the case of a 14-year-old female with new-onset DKA with pH of 6.66, and potassium of 1.6 mEq/L. We started her on careful potassium replacement before starting her on insulin. She had a great prognosis without any complications. Our case presents the lowest level of pH ever reported in a survived pediatric DKA patient. We emphasize the importance of careful management of hypokalemia in patients with severe depletion. Potassium therapy with careful fluid management must be initiated prior to insulin therapy to prevent cardiac completions from hypokalemia.
Keywords: diabetic ketoacidosis; hypokalemia; insulin; pediatric.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Wolfsdorf JI, Allgrove J, Craig M, Edge J. Hyperglycemic crises in pediatric patients with diabetes: a consensus statement from the International Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2014;20(suppl 20):154-179.
-
- Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Murphy MB, et al. Hypergly-cemic crises in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(suppl 1):S94-S102. - PubMed
-
- Adrogue HJ, Madias NE. Changes in plasma potassium concentration during acute acid-base disturbances. Am J Med. 1981;71:456-467. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous