A Computational Model of the Escape Response Latency in the Giant Fiber System of Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 31001574
- PMCID: PMC6469880
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0423-18.2019
A Computational Model of the Escape Response Latency in the Giant Fiber System of Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
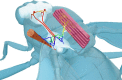
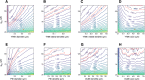
The giant fiber system (GFS) is a multi-component neuronal pathway mediating rapid escape response in the adult fruit-fly Drosophila melanogaster, usually in the face of a threatening visual stimulus. Two branches of the circuit promote the response by stimulating an escape jump followed by flight initiation. A recent work demonstrated an age-associated decline in the speed of signal propagation through the circuit, measured as the stimulus-to-muscle depolarization response latency. The decline is likely due to the diminishing number of inter-neuronal gap junctions in the GFS of ageing flies. In this work, we presented a realistic conductance-based, computational model of the GFS that recapitulates the experimental results and identifies some of the critical anatomical and physiological components governing the circuit's response latency. According to our model, anatomical properties of the GFS neurons have a stronger impact on the transmission than neuronal membrane conductance densities. The model provides testable predictions for the effect of experimental interventions on the circuit's performance in young and ageing flies.
Keywords: Drosophila; aging; computational model; escape response; gap junctions; ion channels.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mutations in shaking-B prevent electrical synapse formation in the Drosophila giant fiber system.J Neurosci. 1996 Feb 1;16(3):1101-13. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-03-01101.1996. J Neurosci. 1996. PMID: 8558239 Free PMC article.
-
Escape flight initiation in the fly.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2007 Apr;193(4):471-6. doi: 10.1007/s00359-006-0203-9. Epub 2007 Jan 13. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17221263
-
Electrophysiological recordings from the Drosophila giant fiber system (GFS).Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2010 Jul 1;2010(7):pdb.prot5453. doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot5453. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2010. PMID: 20647357 Free PMC article.
-
Making an escape: development and function of the Drosophila giant fibre system.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2006 Feb;17(1):31-41. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2005.11.011. Epub 2005 Dec 27. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16378740 Review.
-
Functional senescence in Drosophila melanogaster.Ageing Res Rev. 2005 Aug;4(3):372-97. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2005.04.001. Ageing Res Rev. 2005. PMID: 16024299 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence for Prepulse Inhibition of Visually Evoked Motor Response in Drosophila melanogaster.Biology (Basel). 2023 Apr 21;12(4):635. doi: 10.3390/biology12040635. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37106835 Free PMC article.
-
Interlocked transcription factor feedback loops maintain and restore touch sensation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 20:2025.05.15.654349. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.15.654349. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40475441 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Distinct Aging-Vulnerable and -Resilient Trajectories of Specific Motor Circuit Functions in Oxidation- and Temperature-Stressed Drosophila.eNeuro. 2022 Jan 19;9(1):ENEURO.0443-21.2021. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0443-21.2021. Print 2022 Jan-Feb. eNeuro. 2022. PMID: 34876473 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling aging and its impact on cellular function and organismal behavior.Exp Gerontol. 2021 Nov;155:111577. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2021.111577. Epub 2021 Sep 26. Exp Gerontol. 2021. PMID: 34582969 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bennett MV (1997) Gap junctions as electrical synapses. J Neurocytol 26:349–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
