Early signs of middle cerebral artery infarction on multidetector computed tomography: Review of 20 cases
- PMID: 31001598
- PMCID: PMC6458774
- DOI: 10.4103/bc.bc_28_18
Early signs of middle cerebral artery infarction on multidetector computed tomography: Review of 20 cases
Abstract
Objective: This study intended to assess the occurrence of early signs of middle cerebral artery (MCA) on multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) in correlation with duration of the clinical features of stroke.
Patients and methods: This retrospective study analyzed the electronic records of 20 patients with MCA infarction. The detected signs studied according to the onset of the clinical features of stroke to the time of CT imaging.
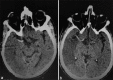
Results: Out of 20 patients with MCA infarction included in this study, the results revealed a significant relationship between the presence of insular ribbon sign and/or subtle hypodensity and hyperacute infarction (P < 0.001 and 0.003, respectively). Results revealed significant relationship between the occurrence of hypodense area, effacement of the cortical sulci, and compression of the ipsilateral lateral ventricle with acute infarction (6-72 h), (P = 0.006, 0.007, and 0.002) (odds ratio = 0.047, 0.050 and 0.028) and (95% confidence interval = 0.004-0.552, 0.004-0.597 and 0.002-0.367) respectively.
Conclusion: MDCT can detect nearly half of MCA infarctions in the first 6 h. Insular ribbon sign and subtle hypodensity were the most significant findings in the first 6 h of stroke. Hypodense area was a significant sign after 6 h. Diabetes mellitus and ischemic heart disease were the most common risk factors. Hemiparesis was the most common clinical finding in MCA infarction.
Keywords: Early signs; middle cerebral artery infarction; multidetector computed tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early CT signs in patients with acute middle cerebral artery occlusion: incidence of contrast staining and haemorrhagic transformations after intra-arterial reperfusion therapy.Clin Radiol. 2006 Feb;61(2):156-62. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2005.08.016. Clin Radiol. 2006. PMID: 16439221
-
Loss of the insular ribbon: another early CT sign of acute middle cerebral artery infarction.Radiology. 1990 Sep;176(3):801-6. doi: 10.1148/radiology.176.3.2389039. Radiology. 1990. PMID: 2389039
-
Early CT signs in acute middle cerebral artery infarction: predictive value for subsequent infarct locations and outcome.Neurology. 1996 Aug;47(2):366-75. doi: 10.1212/wnl.47.2.366. Neurology. 1996. PMID: 8757006
-
[Brain CT scan for acute cerebral infarction: early signs of ischemia].Rev Neurol (Paris). 1999;155(9):649-55. Rev Neurol (Paris). 1999. PMID: 10528343 Review. French.
-
Malignant MCA Infarction: Pathophysiology and Imaging for Early Diagnosis and Management Decisions.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016;41(1-2):1-7. doi: 10.1159/000441627. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016. PMID: 26581023 Review.
Cited by
-
Occurrence of malignant cerebral infarction following intracranial hematoma evacuation in traumatic brain injury: A case report.Surg Neurol Int. 2024 Sep 27;15:349. doi: 10.25259/SNI_629_2024. eCollection 2024. Surg Neurol Int. 2024. PMID: 39372989 Free PMC article.
-
Continuum topological derivative - A novel application tool for segmentation of CT and MRI images.Neuroimage Rep. 2024 Aug 1;4(3):100215. doi: 10.1016/j.ynirp.2024.100215. eCollection 2024 Sep. Neuroimage Rep. 2024. PMID: 40568569 Free PMC article.
-
Does radiological conjugate eye deviation sign play a role in acute stroke imaging? A meta-analysis.J Neurol. 2022 Mar;269(3):1142-1153. doi: 10.1007/s00415-021-10540-7. Epub 2021 Apr 11. J Neurol. 2022. PMID: 33839904 Review.
-
Role of decompressive craniectomy in the management of acute ischemic stroke (Review).Biomed Rep. 2024 Jan 3;20(2):33. doi: 10.3892/br.2024.1721. eCollection 2024 Feb. Biomed Rep. 2024. PMID: 38273901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation between clinical and brain computed tomography findings of stroke patients: A cross-sectional study.Health Sci Rep. 2023 May 3;6(5):e1248. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1248. eCollection 2023 May. Health Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37152223 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Islam MN, Kuddus R, Chowdhury NS, Akhter MD, Salahuddin G, Parvin S, et al. Radiologic evaluation of hyperacute brain infarction: A review. Mymensingh Med J. 2014;23:621–35. - PubMed

