Inter- and intra-reader agreement for gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI parameter readings in patients with chronic liver diseases
- PMID: 31001679
- PMCID: PMC6828941
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-019-06182-z
Inter- and intra-reader agreement for gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI parameter readings in patients with chronic liver diseases
Abstract
Objectives: To examine inter- and intra-observer agreement for four simple hepatobiliary phase (HBP)-based scores on gadoxetic acid (GA)-enhanced MRI and their correlation with liver function in patients with mixed chronic liver disease (CLD).
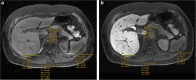
Methods: This single-center, retrospective study included 287 patients (62% male, 38% female, mean age 53.5 ± 13.7 years) with mixed CLD (20.9% hepatitis C, 19.2% alcoholic liver disease, 8% hepatitis B) who underwent GA-enhanced MRI of the liver for clinical care between 2010 and 2015. Relative liver enhancement (RLE), contrast uptake index (CUI), hepatic uptake index (HUI), and liver-to-spleen contrast index (LSI) were calculated by two radiologists independently using unenhanced and GA-enhanced HPB (obtained 20 min after GA administration) images; 50 patients selected at random were reviewed twice by one reader to assess intra-observer reliability. Agreement was assessed by intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). The albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) score, the model of end-stage liver disease (MELD), and the Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) score were calculated as standards of reference for hepatic function.
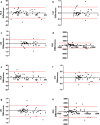
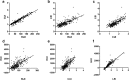
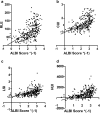
Results: Intra-observer ICCs ranged from 0.814 (0.668-0.896) for CUI to 0.969 (0.945-0.983) for RLE. Inter-observer ICCs ranged from 0.777 (0.605-0.874) for HUI to 0.979 (0.963-0.988) for RLE. All HBP-based scores correlated significantly (all p < 0.001) with the ALBI, MELD, and CTP scores and were able to discriminate patients with a MELD score ≥ 15 versus ≤ 14, with area under the curve values ranging from 0.760 for RLE to 0.782 for HUI.
Conclusion: GA-enhanced, MRI-derived, HBP-based parameters showed excellent inter- and intra-observer agreement. All HBP-based parameters correlated with clinical and laboratory scores of hepatic dysfunction, with no significant differences between each other.
Key points: • Radiological parameters that quantify the hepatic uptake of gadoxetic acid are highly reproducible. • These parameters can be used interchangeably because they correlate with each other and with scores of hepatic dysfunction. • Assessment of these parameters may be helpful in monitoring disease progression.
Keywords: Gadoxetic acid; Liver; Liver diseases; Liver function tests; Magnetic resonance imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures
References
-
- Kochanek KD, Murphy SL (2016) National Vital Statistic Report 65
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

