Cholesterol 24-Hydroxylation by CYP46A1: Benefits of Modulation for Brain Diseases
- PMID: 31001737
- PMCID: PMC6694357
- DOI: 10.1007/s13311-019-00731-6
Cholesterol 24-Hydroxylation by CYP46A1: Benefits of Modulation for Brain Diseases
Abstract
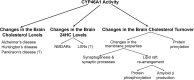
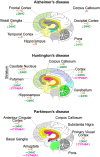
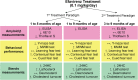
Cholesterol 24-hydroxylation is the major mechanism for cholesterol removal from the brain and the reaction catalyzed by cytochrome P450 46A1 (CYP46A1), a CNS-specific enzyme. This review describes CYP46A1 in the context of cholesterol homeostasis in the brain and summarizes available experimental data on CYP46A1 association with different neurologic diseases, including the mechanisms by which changes in the CYP46A1 activity in the brain could be beneficial for these diseases. The modulation of CYP46A1 activity by genetic and pharmacologic means is also presented along with a brief synopsis of the two clinical trials that evaluate CYP46A1 as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease as well as Dravet and Lennox-Gastaut syndromes.
Keywords: 24-Hydroxycholesterol; CYP46A1; Cholesterol; Cholesterol turnover; Efavirenz; Neurodegeneration.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cholesterol-metabolizing enzyme cytochrome P450 46A1 as a pharmacologic target for Alzheimer's disease.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Sep 1;123:465-476. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.06.026. Epub 2017 Jun 24. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28655608 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Acetyl-CoA Production and Phosphorylation of Cytoskeletal Proteins Are Targets of CYP46A1 Activity Modulation and Altered Sterol Flux.Neurotherapeutics. 2021 Jul;18(3):2040-2060. doi: 10.1007/s13311-021-01079-6. Epub 2021 Jul 7. Neurotherapeutics. 2021. PMID: 34235635 Free PMC article.
-
CYP46A1 Activation by Efavirenz Leads to Behavioral Improvement without Significant Changes in Amyloid Plaque Load in the Brain of 5XFAD Mice.Neurotherapeutics. 2019 Jul;16(3):710-724. doi: 10.1007/s13311-019-00737-0. Neurotherapeutics. 2019. PMID: 31062296 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol 24-hydroxylase: Brain cholesterol metabolism and beyond.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Dec;1861(12 Pt A):1911-1920. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.09.011. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27663182 Review.
-
The potential of CYP46A1 as a novel therapeutic target for neurological disorders: An updated review of mechanisms.Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 15;949:175726. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175726. Epub 2023 Apr 14. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37062503 Review.
Cited by
-
Kiaa1024L/Minar2 is essential for hearing by regulating cholesterol distribution in hair bundles.Elife. 2022 Nov 1;11:e80865. doi: 10.7554/eLife.80865. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36317962 Free PMC article.
-
Association between aromatic amines and serum neurofilament light chain as a biomarker of neural damage: a cross-sectional study from NHANES.Front Public Health. 2024 Sep 24;12:1344087. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1344087. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39381758 Free PMC article.
-
Oxysterols in Central and Peripheral Synaptic Communication.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1440:91-123. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-43883-7_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38036877
-
The Intersection of cerebral cholesterol metabolism and Alzheimer's disease: Mechanisms and therapeutic prospects.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 30;10(9):e30523. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30523. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38726205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholesterol metabolism: physiological versus pathological aspects in intracerebral hemorrhage.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Apr 1;20(4):1015-1030. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01462. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 38989934 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dietschy JM, Turley SD. Thematic review series: brain Lipids. Cholesterol metabolism in the central nervous system during early development and in the mature animal. J Lipid Res. 2004;45:1375–1397. - PubMed
-
- Dietschy JM, Turley SD. Cholesterol metabolism in the brain. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2001;12:105–112. - PubMed
-
- Pfrieger FW, Ungerer N. Cholesterol metabolism in neurons and astrocytes. Prog Lipid Res. 2011;50:357–371. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

