Cholesterol 24-Hydroxylation by CYP46A1: Benefits of Modulation for Brain Diseases
- PMID: 31001737
- PMCID: PMC6694357
- DOI: 10.1007/s13311-019-00731-6
Cholesterol 24-Hydroxylation by CYP46A1: Benefits of Modulation for Brain Diseases
Abstract
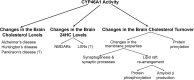
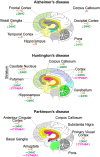
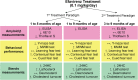
Cholesterol 24-hydroxylation is the major mechanism for cholesterol removal from the brain and the reaction catalyzed by cytochrome P450 46A1 (CYP46A1), a CNS-specific enzyme. This review describes CYP46A1 in the context of cholesterol homeostasis in the brain and summarizes available experimental data on CYP46A1 association with different neurologic diseases, including the mechanisms by which changes in the CYP46A1 activity in the brain could be beneficial for these diseases. The modulation of CYP46A1 activity by genetic and pharmacologic means is also presented along with a brief synopsis of the two clinical trials that evaluate CYP46A1 as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease as well as Dravet and Lennox-Gastaut syndromes.
Keywords: 24-Hydroxycholesterol; CYP46A1; Cholesterol; Cholesterol turnover; Efavirenz; Neurodegeneration.
Figures


References
-
- Dietschy JM, Turley SD. Thematic review series: brain Lipids. Cholesterol metabolism in the central nervous system during early development and in the mature animal. J Lipid Res. 2004;45:1375–1397. - PubMed
-
- Dietschy JM, Turley SD. Cholesterol metabolism in the brain. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2001;12:105–112. - PubMed
-
- Pfrieger FW, Ungerer N. Cholesterol metabolism in neurons and astrocytes. Prog Lipid Res. 2011;50:357–371. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

