The once-daily fixed-dose combination of olodaterol and tiotropium in the management of COPD: current evidence and future prospects
- PMID: 31002020
- PMCID: PMC6475840
- DOI: 10.1177/1753466619843426
The once-daily fixed-dose combination of olodaterol and tiotropium in the management of COPD: current evidence and future prospects
Abstract
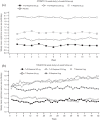
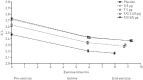
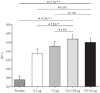
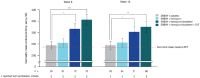
Long-acting bronchodilators are the cornerstone of pharmacologic treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Spiolto® or Stiolto® is a fixed-dose combination (FDC) containing two long-acting bronchodilators, the long-acting muscarinic receptor antagonist tiotropium (TIO) and the long-acting β2-adrenoceptor agonist olodaterol (OLO), formulated in the Respimat® Soft Mist™ inhaler. A total of 13 large, multicentre studies of up to 52 weeks' duration have documented its efficacy in more than 15,000 patients with COPD. TIO/OLO 5/5 µg FDC significantly increases pulmonary function compared with placebo and its respective constituent mono-components TIO 5 µg and OLO 5 µg. TIO/OLO 5/5 µg also results in statistically and clinically significant improvements in patient-reported outcomes, such as dyspnoea, use of rescue medication, and health status. Addition of OLO 5 µg to TIO 5 µg reduces the rate of moderate-to-severe exacerbations by approximately 10%. Compared with placebo and TIO 5 µg, TIO/OLO 5/5 µg significantly improves exercise capacity (e.g. endurance time) and physical activity, the latter increase being reached by a unique combination behavioural modification intervention, dual bronchodilatation and exercise training. Overall, the likelihood for patients to experience a clinically significant benefit is higher with TIO/OLO 5/5 µg than with its constituent mono-components, which usually yield smaller improvements which do not always reach statistical significance, compared with baseline or placebo. This supports the early introduction of TIO/OLO 5/5 µg in the management of patients with symptomatic COPD.
Keywords: COPD; LABA; LAMA; bronchodilatation; dyspnoea; exacerbation; exercise tolerance; hyperinflation; inspiratory capacity; physical activity; spirometry.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of tiotropium and olodaterol in COPD: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Respir Res. 2017 Nov 25;18(1):196. doi: 10.1186/s12931-017-0683-x. Respir Res. 2017. PMID: 29178871 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of tiotropium-olodaterol fixed-dose combination in COPD.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016 Dec 13;11:3163-3177. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S92840. eCollection 2016. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2016. PMID: 28008243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences in Real-World Health and Economic Outcomes Among Patients with COPD Treated with Combination Tiotropium/Olodaterol Versus Triple Therapy.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2020 Oct;26(10):1363-1374. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2020.20159. Epub 2020 Jul 17. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32678719 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Efficacy of Once-Daily Umeclidinium/Vilanterol and Tiotropium/Olodaterol Therapy in Symptomatic Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Randomized Study.Adv Ther. 2017 Nov;34(11):2518-2533. doi: 10.1007/s12325-017-0626-4. Epub 2017 Nov 1. Adv Ther. 2017. PMID: 29094315 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of rescue medication use and medication adherence receiving umeclidinium/vilanterol versus tiotropium bromide/olodaterol.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019 Sep 4;14:2047-2060. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S213520. eCollection 2019. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2019. PMID: 31564852 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Effectiveness Using Different Dual Bronchodilator Agents in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Treatment.J Clin Med. 2021 Jun 16;10(12):2649. doi: 10.3390/jcm10122649. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34208599 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra Long-Acting β-Agonists in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.J Exp Pharmacol. 2020 Dec 14;12:589-602. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S259328. eCollection 2020. J Exp Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33364854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-world effectiveness of early intervention with fixed-dose tiotropium/olodaterol vs tiotropium in Japanese patients with COPD: a high-dimensional propensity score-matched cohort analysis.Respir Res. 2021 Jun 17;22(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12931-021-01776-y. Respir Res. 2021. PMID: 34140019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agusti A, Vogelmeier C. Global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; (updated 2019). Report 2019.
-
- Lopez-Campos JL, Tan W, Soriano JB. Global burden of COPD. Respirology (Carlton, Vic) 2016; 21: 14–23. - PubMed
-
- Ford ES, Murphy LB, Khavjou O, et al. Total and state-specific medical and absenteeism costs of COPD among adults aged ⩾18 years in the United States for 2010 and projections through 2020. Chest 2015; 147: 31–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

