Inhibition of neddylation modification by MLN4924 sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib
- PMID: 31002342
- PMCID: PMC6489087
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2019.7098
Inhibition of neddylation modification by MLN4924 sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib
Retraction in
-
[Retracted] Inhibition of neddylation modification by MLN4924 sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib.Oncol Rep. 2025 Mar;53(3):33. doi: 10.3892/or.2025.8866. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Oncol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39821334 Free PMC article.
Abstract
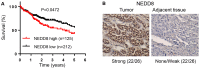
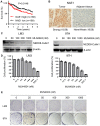
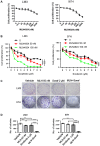
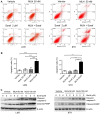
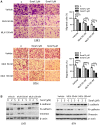
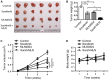
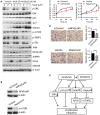
Sorafenib remains the standard care for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) even though it has low antitumor efficacy. Protein neddylation is abnormally activated in many types of human cancer. However, whether dysregulation of neddylation is involved in HCC progression and whether targeting neddylation sensitizes HCC cells to sorafenib need to be ascertained. In the present study, it was demonstrated that high expression of neddylation components, neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally downregulated 8 (NEDD8) and NEDD8‑activating enzyme 1 (NAE1), were associated with poor survival of patients with HCC. Inhibition of neddylation by MLN4924, a small‑molecule inhibitor of NAE1, significantly inhibited HCC growth, reduced clonogenic survival, increased apoptosis, and decreased migration capacity. Sorafenib alone exhibited minimal anticancer efficacy. However, a combination of sorafenib with MLN4924 at a low concentration significantly enhanced the inhibition of cell proliferation and migration as well as the induction of apoptosis induced by sorafenib. In vivo HCC xenograft mouse models also showed that MLN4924 increased the antitumor efficacy of sorafenib. Mechanistically, MLN4924 enhanced the antitumor activity of sorafenib in HCC cells via upregulation of cullin‑RING E3 ubiquitin ligase (CRL)/Skp1‑Cullin1‑F box (SCF) E3 ubiquitin ligase substrates p21, p27, Deptor and IκBɑ. Taken together, these findings suggest that combination therapy of MLN4924 with sorafenib appears to present an additive effect with a maximal in the treatment of HCC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of Neddylation Modification Sensitizes Pancreatic Cancer Cells to Gemcitabine.Neoplasia. 2017 Jun;19(6):509-518. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2017.04.003. Epub 2017 May 20. Neoplasia. 2017. PMID: 28535453 Free PMC article.
-
Neddylation Blockade Diminishes Hepatic Metastasis by Dampening Cancer Stem-Like Cells and Angiogenesis in Uveal Melanoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Aug 1;24(15):3741-3754. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1703. Epub 2017 Dec 12. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29233905
-
MLN4924, a novel protein neddylation inhibitor, suppresses proliferation and migration of human urothelial carcinoma: In vitro and in vivo studies.Cancer Lett. 2015 Jul 28;363(2):127-36. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.01.015. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 25615422
-
Targeting Neddylation pathways to inactivate cullin-RING ligases for anticancer therapy.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014 Dec 10;21(17):2383-400. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5795. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014. PMID: 24410571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel approach to explore metabolic diseases: Neddylation.Pharmacol Res. 2024 Dec;210:107532. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107532. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Pharmacol Res. 2024. PMID: 39637955 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of neddylation on viral infection: an overview.Arch Virol. 2023 Dec 11;169(1):6. doi: 10.1007/s00705-023-05930-3. Arch Virol. 2023. PMID: 38081982 Review.
-
SerpinB3 Differently Up-Regulates Hypoxia Inducible Factors -1α and -2α in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Mechanisms Revealing Novel Potential Therapeutic Targets.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Dec 4;11(12):1933. doi: 10.3390/cancers11121933. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31817100 Free PMC article.
-
Neddylation: A Versatile Pathway Takes on Chronic Liver Diseases.Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Oct 19;7:586881. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.586881. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33195347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NUB1 reduction promotes PCNA-mediated tumor growth by disturbing the PCNA polyubiquitination/NEDDylation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Mar 31;16(1):228. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07567-3. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40164590 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Neddylation Blockade on Slug-Dependent Cancer Cell Migration Is Regulated by p53 Mutation Status.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 30;13(3):531. doi: 10.3390/cancers13030531. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33573293 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goyal L, Zheng H, Abrams TA, Miksad R, Bullock AJ, Allen JN, Yurgelun MB, Clark JW, Kambadakone A, Muzikansky A, et al. A phase II and biomarker study of sorafenib combined with modified FOLFOX in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:80–89. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-0847. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

