Maspin differential expression patterns as a potential marker for targeted screening of esophageal adenocarcinoma/gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 31002675
- PMCID: PMC6474598
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215089
Maspin differential expression patterns as a potential marker for targeted screening of esophageal adenocarcinoma/gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Aim: Barrett's esophagus (BE) is a predisposing factor of esophageal adenocarcinoma/gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (ECA/GEJ Aca). BE patients are stratified and subsequently monitored according to the risk of malignant progression by the combination of endoscopy and biopsy. This study is to evaluate the maspin expression patterns as early diagnostic markers of malignancy in BE patients.
Materials and methods: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining was performed on 62 archival core biopsies from 35 patients, including BE without dysplasia (intestinal metaplasia, IM), BE with low grade dysplasia, BE with high grade dysplasia, carcinoma in situ, and well to poorly differentiated ECA/GEJ Aca (PD-ECA/GEJ Aca). The intensity and the subcellular distribution of immunoreactivity were evaluated microscopically. Statistical analysis was performed using the χ2 and Fisher exact tests.
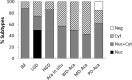
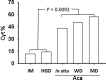
Results: The level of epithelial-specific tumor suppressor maspin protein inversely correlated with the progression from IM to PD-ECA/GEJ Aca. Lesions of each pathological grade could be divided into subtypes that exhibited distinct maspin subcellular distribution patterns, including nuclear only (Nuc), combined nuclear and cytoplasmic (Nuc+Cyt), cytoplasmic only (Cyt) and overall negligible (Neg). The Cyt subtype, which was minor in both IM and dysplasia (approximately 10%), was predominant in ECA/GEJ Aca as early as well-differentiated lesions (more than 50%: p = 0.0092). In comparison, nuclear staining of the tumor suppressor TP53 was heterogeneous in dysplasia, and did not correlate with the differentiation grades of ECA/GEJ Aca.
Conclusion: The Cyt subtype of maspin expression pattern in core biopsies of BE patients may serve as a molecular marker for early diagnosis of ECA/GEJ Aca.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

