Broad domains of histone 3 lysine 4 trimethylation are associated with transcriptional activation in CA1 neurons of the hippocampus during memory formation
- PMID: 31002880
- PMCID: PMC6541021
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2019.04.009
Broad domains of histone 3 lysine 4 trimethylation are associated with transcriptional activation in CA1 neurons of the hippocampus during memory formation
Abstract
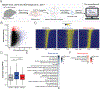
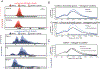
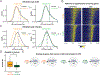
Transcriptional changes in the hippocampus are required for memory formation, and these changes are regulated by numerous post-translational modifications of chromatin-associated proteins. One of the epigenetic marks that has been implicated in memory formation is histone 3 lysine 4 trimethylation (H3K4me3), and this modification is found at the promoters of actively transcribed genes. The total levels of H3K4me3 are increased in the CA1 region of the hippocampus during memory formation, and genetic perturbation of the K4 methyltransferases and demethylases interferes with forming memories. Previous chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by deep sequencing (ChIP-seq) analyses failed to detect changes in H3K4me3 levels at the promoters of memory-linked genes. Since the breadth of H3K4me3 marks was recently reported to be associated with the transcriptional outcome of a gene, we re-analyzed H3K4me3 ChIP-seq data sets to identify the role of H3K4me3 broad domains in CA1 neurons, as well as identify differences in breadth that occur during contextual fear conditioning. We found that, under baseline conditions, broad H3K4me3 peaks mark important learning and memory genes and are often regulated by super-enhancers. The peaks at many learning-associated genes become broader during novel environment exposure and memory formation. Furthermore, the important learning- and memory-associated lysine methyltransferases, Kmt2a and Kmt2b, are involved in maintaining H3K4me3 peak width. Our findings highlight the importance of analyzing H3K4me3 peak shape, and demonstrate that breadth of H3K4me3 marks in neurons of the hippocampus is regulated during memory formation.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Epigenetics; Hippocampus; Histone methylation; Memory; Transcription.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
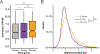

References
-
- Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh TY, Schones DE, Wang Z, Wei G, Chepelev I, & Zhao K (2007). High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell, 129, 823–837. - PubMed
-
- Benayoun BA, Pollina EA, Ucar D, Mahmoudi S, Karra K, Wong ED, Devarajan K, Daugherty AC, Kundaje AB, Mancini E, Hitz BC, Gupta R, Rando TA, Baker JC, Snyder MP, Cherry JM, & Brunet A (2014). H3K4me3 breadth is linked to cell identity and transcriptional consistency. Cell, 158, 673–688. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

