GLP-1: Molecular mechanisms and outcomes of a complex signaling system
- PMID: 31002893
- PMCID: PMC7081944
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuint.2019.04.010
GLP-1: Molecular mechanisms and outcomes of a complex signaling system
Abstract
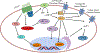
Meal ingestion provokes the release of hormones and transmitters, which in turn regulate energy homeostasis and feeding behavior. One such hormone, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), has received significant attention in the treatment of obesity and diabetes due to its potent incretin effect. In addition to the peripheral actions of GLP-1, this hormone is able to alter behavior through the modulation of multiple neural circuits. Recent work that focused on elucidating the mechanisms and outcomes of GLP-1 neuromodulation led to the discovery of an impressive array of GLP-1 actions. Here, we summarize the many levels at which the GLP-1 signal adapts to different systems, with the goal being to provide a background against which to guide future research.
Keywords: Bariatric surgery; Feeding behavior; Glucagon-like peptide-1; Reward.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Ahrén B, 2004. Sensory nerves contribute to insulin secretion by glucagon-like peptide-1 in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol 286, R269–R272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

