Real-Time Classification of Multivariate Olfaction Data Using Spiking Neural Networks
- PMID: 31003417
- PMCID: PMC6515392
- DOI: 10.3390/s19081841
Real-Time Classification of Multivariate Olfaction Data Using Spiking Neural Networks
Abstract
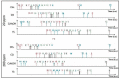
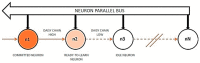
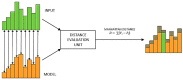
Recent studies in bioinspired artificial olfaction, especially those detailing the application of spike-based neuromorphic methods, have led to promising developments towards overcoming the limitations of traditional approaches, such as complexity in handling multivariate data, computational and power requirements, poor accuracy, and substantial delay for processing and classification of odors. Rank-order-based olfactory systems provide an interesting approach for detection of target gases by encoding multi-variate data generated by artificial olfactory systems into temporal signatures. However, the utilization of traditional pattern-matching methods and unpredictable shuffling of spikes in the rank-order impedes the performance of the system. In this paper, we present an SNN-based solution for the classification of rank-order spiking patterns to provide continuous recognition results in real-time. The SNN classifier is deployed on a neuromorphic hardware system that enables massively parallel and low-power processing on incoming rank-order patterns. Offline learning is used to store the reference rank-order patterns, and an inbuilt nearest neighbor classification logic is applied by the neurons to provide recognition results. The proposed system was evaluated using two different datasets including rank-order spiking data from previously established olfactory systems. The continuous classification that was achieved required a maximum of 12.82% of the total pattern frame to provide 96.5% accuracy in identifying corresponding target gases. Recognition results were obtained at a nominal processing latency of 16ms for each incoming spike. In addition to the clear advantages in terms of real-time operation and robustness to inconsistent rank-orders, the SNN classifier can also detect anomalies in rank-order patterns arising due to drift in sensing arrays.
Keywords: SNN-based classification; bioinspired artificial olfaction; electronic nose systems; multi-variate data classification; neuromorphic olfaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
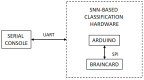
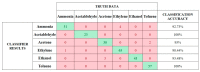
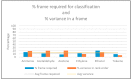
Similar articles
-
Application of Neuromorphic Olfactory Approach for High-Accuracy Classification of Malts.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 7;22(2):440. doi: 10.3390/s22020440. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35062402 Free PMC article.
-
A Hardware-Deployable Neuromorphic Solution for Encoding and Classification of Electronic Nose Data.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Nov 6;19(22):4831. doi: 10.3390/s19224831. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31698785 Free PMC article.
-
Application of a Brain-Inspired Spiking Neural Network Architecture to Odor Data Classification.Sensors (Basel). 2020 May 12;20(10):2756. doi: 10.3390/s20102756. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32408563 Free PMC article.
-
An Investigation into Spike-Based Neuromorphic Approaches for Artificial Olfactory Systems.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Nov 10;17(11):2591. doi: 10.3390/s17112591. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29125586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in Algorithms and Neuromorphic Hardware for Spiking Neural Networks.Neural Comput. 2022 May 19;34(6):1289-1328. doi: 10.1162/neco_a_01499. Neural Comput. 2022. PMID: 35534005 Review.
Cited by
-
Visual Analysis of Odor Interaction Based on Support Vector Regression Method.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Mar 19;20(6):1707. doi: 10.3390/s20061707. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32204317 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Optimized Spiking Neural Network Architectures for Classification Tasks on Embedded Platforms.Sensors (Basel). 2021 May 7;21(9):3240. doi: 10.3390/s21093240. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34067080 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Neuromorphic Olfactory Approach for High-Accuracy Classification of Malts.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 7;22(2):440. doi: 10.3390/s22020440. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35062402 Free PMC article.
-
Optical Axons for Electro-Optical Neural Networks.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Oct 27;20(21):6119. doi: 10.3390/s20216119. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33121207 Free PMC article.
-
A Hardware-Deployable Neuromorphic Solution for Encoding and Classification of Electronic Nose Data.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Nov 6;19(22):4831. doi: 10.3390/s19224831. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31698785 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith L.S. Neuromorphic Systems: Past, Present and Future. In: Hussain A., Aleksander I., Smith L.S., Barros A.K., Chrisley R., Cutsuridis V., editors. Brain Inspired Cognitive Systems 2008. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2010. pp. 167–182. - PubMed
-
- Chicca E., Schmuker M., Nawrot M. Neuromorphic Sensors, Olfaction. In: Jaeger D., Jung R., editors. Encyclopedia of Computational Neuroscience. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2013. pp. 1–7.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

