Oxidative Stress and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation
- PMID: 31003450
- PMCID: PMC6521137
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11040872
Oxidative Stress and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation
Abstract
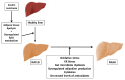
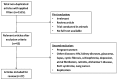
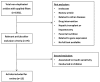
Aging is a complex phenomenon characterized by the progressive loss of tissue and organ function. The oxidative-stress theory of aging postulates that age-associated functional losses are due to the accumulation of ROS-induced damage. Liver function impairment and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are common among the elderly. NAFLD can progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and evolve to hepatic cirrhosis or hepatic carcinoma. Oxidative stress, lipotoxicity, and inflammation play a key role in the progression of NAFLD. A growing body of evidence supports the therapeutic potential of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFA), mainly docosahaexenoic (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), on metabolic diseases based on their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Here, we performed a systematic review of clinical trials analyzing the efficacy of n-3 PUFA on both systemic oxidative stress and on NAFLD/NASH features in adults. As a matter of fact, it remains controversial whether n-3 PUFA are effective to counteract oxidative stress. On the other hand, data suggest that n-3 PUFA supplementation may be effective in the early stages of NAFLD, but not in patients with more severe NAFLD or NASH. Future perspectives and relevant aspects that should be considered when planning new randomized controlled trials are also discussed.
Keywords: aging; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; omega-3 fatty acids; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BFU2015-65937-R/Ministry of Economy, Industry and Competitiveness (MINECO-FEDER). Government of Spain.
- 67-2015/Department of Health of the Navarra Government
- CB12/03/30002/CIBER Physiopathology of Obesity and Nutrition (CIBERobn), Carlos III Health Research Institute
- IJCI-2016-30025/"Juan de la Cierva" Grant. Ministry of Sciences, Innovation and Universities
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

