The Cytoskeleton-A Complex Interacting Meshwork
- PMID: 31003495
- PMCID: PMC6523135
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8040362
The Cytoskeleton-A Complex Interacting Meshwork
Abstract
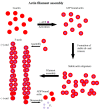
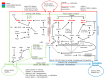
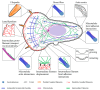
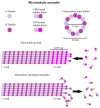
The cytoskeleton of animal cells is one of the most complicated and functionally versatile structures, involved in processes such as endocytosis, cell division, intra-cellular transport, motility, force transmission, reaction to external forces, adhesion and preservation, and adaptation of cell shape. These functions are mediated by three classical cytoskeletal filament types, as follows: Actin, microtubules, and intermediate filaments. The named filaments form a network that is highly structured and dynamic, responding to external and internal cues with a quick reorganization that is orchestrated on the time scale of minutes and has to be tightly regulated. Especially in brain tumors, the cytoskeleton plays an important role in spreading and migration of tumor cells. As the cytoskeletal organization and regulation is complex and many-faceted, this review aims to summarize the findings about cytoskeletal filament types, including substructures formed by them, such as lamellipodia, stress fibers, and interactions between intermediate filaments, microtubules and actin. Additionally, crucial regulatory aspects of the cytoskeletal filaments and the formed substructures are discussed and integrated into the concepts of cell motility. Even though little is known about the impact of cytoskeletal alterations on the progress of glioma, a final point discussed will be the impact of established cytoskeletal alterations in the cellular behavior and invasion of glioma.
Keywords: actin; glioma; intermediate filaments; microtubules; migration; motility; signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

