Preparation of Benzothiazolyl-Decorated Nanoliposomes
- PMID: 31003552
- PMCID: PMC6514897
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24081540
Preparation of Benzothiazolyl-Decorated Nanoliposomes
Abstract
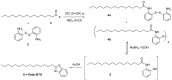
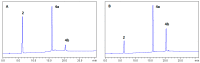
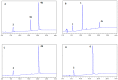
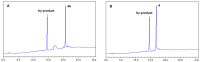
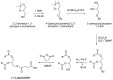
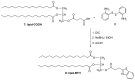
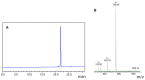
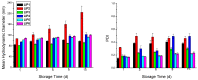
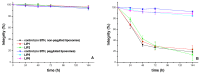
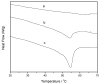
Amyloid β (Aβ) species are considered as potential targets for the development of diagnostics/therapeutics towards Alzheimer's disease (AD). Nanoliposomes which are decorated with molecules having high affinity for Aβ species may be considered as potential carriers for AD theragnostics. Herein, benzothiazolyl (BTH) decorated nanoliposomes were prepared for the first time, after synthesis of a lipidic BTH derivative (lipid-BTH). The synthetic pathway included acylation of bis(2-aminophenyl) disulfide with palmitic acid or palmitoyl chloride and subsequent reduction of the oxidized dithiol derivative. The liberated thiols were able to cyclize to the corresponding benzothiazolyl derivatives only after acidification of the reaction mixture. Each step of the procedure was monitored by HPLC analysis in order to identify all the important parameters for the formation of the BTH-group. Finally, the optimal methodology was identified, and was applied for the synthesis of the lipid-BTH derivative. BTH-decorated nanoliposomes were then prepared and characterized for physicochemical properties (size distribution, surface charge, physical stability, and membrane integrity during incubation in presence of buffer and plasma proteins). Pegylated BTH-nanoliposomes were demonstrated to have high integrity in the presence of proteins (in comparison to non-peglated ones) justifying their further exploitation as potential theragnostic systems for AD.
Keywords: amyloid β; benzothiazoles; functionalization; nanoliposomes; targeting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
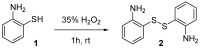
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

