Anisotropic Cellulose Nanofibers/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Graphene Aerogels Fabricated by Directional Freeze-drying as Effective Oil Adsorbents
- PMID: 31003569
- PMCID: PMC6523222
- DOI: 10.3390/polym11040712
Anisotropic Cellulose Nanofibers/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Graphene Aerogels Fabricated by Directional Freeze-drying as Effective Oil Adsorbents
Abstract
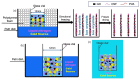
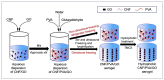
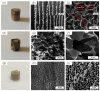
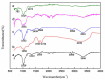
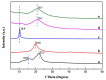
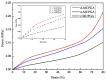
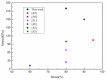
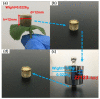
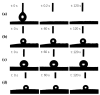
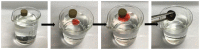
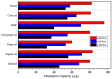
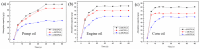
Under the current situation of frequent oil spills, the development of green and recyclable high-efficiency oil-absorbing aerogel materials has attracted wide attention from researchers. In this study, we report a high-strength, three-dimensional hydrophobic cellulose nanofiber (CNF)/polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)/graphene oxide (GO) composite aerogel with an anisotropic porous structure, which was fabricated by directional freeze-drying technology using anisotropically grown ice crystals as a template, followed by hydrophobic treatment with a simple dip coating process. The prepared composite aerogel presented anisotropic multi-level pore microstructures, low density (17.95 mg/cm3) and high porosity (98.8%), good hydrophobicity (water contact angle of 142°) and great adsorption capacity (oil absorption reaching 96 times its own weight). More importantly, the oriented aerogel had high strength, whose compressive stress at 80% strain reached 0.22 MPa and could bear more than 22,123 times its own weight without deformation. Therefore, the CNF/PVA/GO composite aerogel prepared by a simple and easy-to-operate directional freeze-drying method is a promising absorbent for oil-water separation.
Keywords: cellulose nanofibers; directional freeze-drying; graphene; oil absorption; polyvinyl alcohol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Liu H., Geng B., Chen Y., Wang H. A review on the aerogel-type oil sorbents derived from nanocellulose. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016;5:49–66. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b02301. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

