What is the evidence for using bed rest as part of hospital treatment of severe anorexia nervosa?
- PMID: 31003978
- PMCID: PMC10270425
- DOI: 10.1136/ebmental-2018-300064
What is the evidence for using bed rest as part of hospital treatment of severe anorexia nervosa?
Abstract
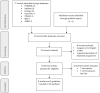
Bed rest is commonly used on medical and paediatric wards as part of nursing management of the physically compromised patient with severe anorexia nervosa. The aim of this study was to review the evidence base of bed rest as an intervention in the management of severe anorexia nervosa. We searched MEDLINE, PubMed, Embase, PsychInfo, CINAHL, HMIC, AMED, HBE, BNI and guidelines written in English until April 2018 using the following terms: bed rest and anorexia nervosa. After exclusion of duplicates, three guidelines and eight articles were included. The papers were methodologically heterogeneous, and therefore, quantitative summary was not possible. There have been no randomised controlled trials to compare the benefits and harms of bed rest as the focus of intervention in the treatment of anorexia nervosa. Several papers showed that patients have a strong preference for less restrictive approaches. These are also less intensive in nursing time. Negative physical consequences were described in a number of studies: these included lower heart rate, impaired bone turn over and increased risk of infection. We found no evidence to support bed rest in hospital treatment of anorexia nervosa. The risks associated with bed rest are significant and include both physical and psychological harm, and these can be avoided by early mobilisation. Given the established complications of bed rest in other critically ill patient populations, it is difficult to recommend the enforcement of bed rest for patients with anorexia nervosa. Future research should focus on safe early mobilisation, which would reduce complications and improve patient satisfaction.
Keywords: adult psychiatry; eating disorders.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inpatient versus outpatient care, partial hospitalisation and waiting list for people with eating disorders.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jan 21;1(1):CD010827. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010827.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30663033 Free PMC article.
-
The ability of low-magnitude mechanical signals to normalize bone turnover in adolescents hospitalized for anorexia nervosa.Osteoporos Int. 2017 Apr;28(4):1255-1263. doi: 10.1007/s00198-016-3851-9. Epub 2016 Dec 1. Osteoporos Int. 2017. PMID: 27909781 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of bed rest on bone turnover in young women hospitalized for anorexia nervosa: a pilot study.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009 May;94(5):1650-5. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-1654. Epub 2009 Feb 17. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 19223524 Free PMC article.
-
[Management of anorexia nervosa in a Tunisian case].Tunis Med. 2014 Jul;92(7):501-3. Tunis Med. 2014. PMID: 25775292 French.
-
Management of eating disorders.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2006 Apr;(135):1-166. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2006. PMID: 17628126 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacotherapy, alternative and adjunctive therapies for eating disorders: findings from a rapid review.J Eat Disord. 2023 Jul 6;11(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s40337-023-00833-9. J Eat Disord. 2023. PMID: 37415200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resistance training is an underused and promising tool in eating disorder recovery: a narrative review.J Eat Disord. 2025 Jul 1;13(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s40337-025-01305-y. J Eat Disord. 2025. PMID: 40597420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physical Fitness-Not Physical Activity Levels-Influence Quality of Life in Anorexia Nervosa.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Feb 25;19(5):2678. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19052678. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35270370 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hall A. Treatment of anorexia nervosa. N Z Med J 1975;82:10–13. - PubMed
-
- NICE. Eating disorders core interventions in the treatment and management of anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and related eating disorders. CG9. London: National Institute of Clinical Excellence, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Royal College of Psychiatrists. MARSIPAN: management of really sick patients with anorexia nervosa. 2 edn, 2014:CR189.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous