Mode of Action of GH30-7 Reducing-End Xylose-Releasing Exoxylanase A (Xyn30A) from the Filamentous Fungus Talaromyces cellulolyticus
- PMID: 31003983
- PMCID: PMC6581162
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00552-19
Mode of Action of GH30-7 Reducing-End Xylose-Releasing Exoxylanase A (Xyn30A) from the Filamentous Fungus Talaromyces cellulolyticus
Abstract
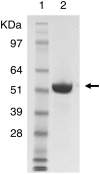
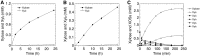
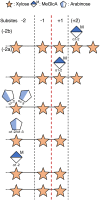
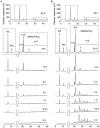
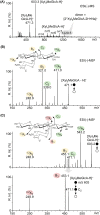
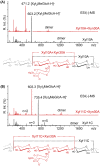
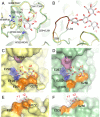
In this study, we characterized the mode of action of reducing-end xylose-releasing exoxylanase (Rex), which belongs to the glycoside hydrolase family 30-7 (GH30-7). GH30-7 Rex, isolated from the cellulolytic fungus Talaromyces cellulolyticus (Xyn30A), exists as a dimer. The purified Xyn30A released xylose from linear xylooligosaccharides (XOSs) 3 to 6 xylose units in length with similar kinetic constants. Hydrolysis of branched, borohydride-reduced, and p-nitrophenyl XOSs clarified that Xyn30A possesses a Rex activity. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR) analysis of xylotriose hydrolysate indicated that Xyn30A degraded XOSs via a retaining mechanism and without recognizing an anomeric structure at the reducing end. Hydrolysis of xylan by Xyn30A revealed that the enzyme continuously liberated both xylose and two types of acidic XOSs: 22-(4-O-methyl-α-d-glucuronyl)-xylotriose (MeGlcA2Xyl3) and 22-(MeGlcA)-xylobiose (MeGlcA2Xyl2). These acidic products were also detected during hydrolysis using a mixture of MeGlcA2Xyl n (n = 2 to 14) as the substrate. This indicates that Xyn30A can release MeGlcA2Xyl n (n = 2 and 3) in an exo manner. Comparison of subsites in Xyn30A and GH30-7 glucuronoxylanase using homology modeling suggested that the binding of the reducing-end residue at subsite +2 was partially prevented by a Gln residue conserved in GH30-7 Rex; additionally, the Arg residue at subsite -2b, which is conserved in glucuronoxylanase, was not found in Xyn30A. Our results lead us to propose that GH30-7 Rex plays a complementary role in hydrolysis of xylan by fungal cellulolytic systems.IMPORTANCE Endo- and exo-type xylanases depolymerize xylan and play crucial roles in the assimilation of xylan in bacteria and fungi. Exoxylanases release xylose from the reducing or nonreducing ends of xylooligosaccharides; this is generated by the activity of endoxylanases. β-Xylosidase, which hydrolyzes xylose residues on the nonreducing end of a substrate, is well studied. However, the function of reducing-end xylose-releasing exoxylanases (Rex), especially in fungal cellulolytic systems, remains unclear. This study revealed the mode of xylan hydrolysis by Rex from the cellulolytic fungus Talaromyces cellulolyticus (Xyn30A), which belongs to the glycoside hydrolase family 30-7 (GH30-7). A conserved residue related to Rex activity is found in the substrate-binding site of Xyn30A. These findings will enhance our understanding of the function of GH30-7 Rex in the cooperative hydrolysis of xylan by fungal enzymes.
Keywords: Talaromyces cellulolyticus; exoxylanase; glycoside hydrolase family 30; lignocellulose; xylan; xylooligosaccharide.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

