Phenotypic and Genomic Determinants of Immunotherapy Response Associated with Squamousness
- PMID: 31003990
- PMCID: PMC6548620
- DOI: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0716
Phenotypic and Genomic Determinants of Immunotherapy Response Associated with Squamousness
Abstract
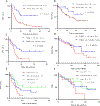
Advanced and metastatic squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) are common and difficult-to-treat malignancies. We assessed 75 immunotherapy-treated patients with SCC from a clinically annotated database of 2,651 patients, as well as 9,407 patients from a deidentified database for molecular features that might influence checkpoint blockade response. SCCs had higher tumor mutational burdens (TMB) than non-SCCs (P < 0.0001). Cutaneous SCCs had the highest TMB (P < 0.0001), with 41.3% demonstrating a very high TMB (≥50 mutations/Mb). In immunotherapy-treated patients with SCC, higher TMB (≥12 mutations/Mb) correlated with a trend to higher clinical benefit rate [stable disease ≥ 6 months or partial/complete remission; 60% vs. 29%; (high vs. low TMB); P = 0.06] and significantly longer median time-to-treatment failure (TTF; 9.9 vs. 4.4 months; P = 0.0058). Cutaneous SCCs had the highest clinical benefit [11/15 patients (73%) vs. 20/60 (33%) non-cutaneous (P = 0.008)], TTF (P = 0.0015), and overall survival (P = 0.06) with immunotherapy treatment. In conclusion, among a diverse set of SCCs, higher TMB and cutaneous disease associated with better immunotherapy outcome.
©2019 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor mutational burden assessed by targeted NGS predicts clinical benefit from immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer.J Pathol. 2020 Jan;250(1):19-29. doi: 10.1002/path.5344. Epub 2019 Oct 24. J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31471895 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Survival and Immune-Related Biomarkers With Immunotherapy in Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-analysis and Individual Patient-Level Analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Jul 3;2(7):e196879. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.6879. JAMA Netw Open. 2019. PMID: 31290993 Free PMC article.
-
Association of TP53 mutations with response and longer survival under immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2019 Jun;132:65-71. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.04.005. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31097096
-
The emerging development of tumor mutational burden in patients with NSCLC.Future Oncol. 2020 Mar;16(9):469-481. doi: 10.2217/fon-2019-0650. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Future Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32048882 Review.
-
Systemic Therapy for Locally Advanced and Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Review.JAMA. 2019 Aug 27;322(8):764-774. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.11058. JAMA. 2019. PMID: 31454018 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the PD-1 Axis with Pembrolizumab for Recurrent or Metastatic Cancer of the Uterine Cervix: A Brief Update.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 11;22(4):1807. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041807. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33670397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction and validation of a prognostic model for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma based on podocyte-associated genes.Cancer Med. 2022 Oct;11(19):3549-3562. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4733. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Cancer Med. 2022. PMID: 35373928 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between tumor mutational burden and maximum standardized uptake value in 2-[18F]FDG PET (positron emission tomography) scan in cancer patients.EJNMMI Res. 2020 Dec 9;10(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s13550-020-00732-z. EJNMMI Res. 2020. PMID: 33296034 Free PMC article.
-
STK11 alterations in the pan-cancer setting: prognostic and therapeutic implications.Eur J Cancer. 2021 May;148:215-229. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.01.050. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Eur J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33744718 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage triggers squamous metaplasia in human lung and mammary cells via mitotic checkpoints.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Jan 21;9(1):21. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01330-3. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 36681661 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brantsch KD, Meisner C, Schönfisch B, Trilling B, Wehner-Caroli J, Röcken M, et al. Analysis of risk factors determining prognosis of cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma: a prospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9:713–20. - PubMed
-
- Maubec E, Petrow P, Scheer-Senyarich I, Duvillard P, Lacroix L, Gelly J, et al. Phase II study of cetuximab as first-line single-drug therapy in patients with unresectable squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:3419–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

