Antagonism between the RNA-binding protein Musashi1 and miR-137 and its potential impact on neurogenesis and glioblastoma development
- PMID: 31004009
- PMCID: PMC6573790
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.069211.118
Antagonism between the RNA-binding protein Musashi1 and miR-137 and its potential impact on neurogenesis and glioblastoma development
Abstract
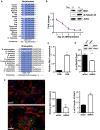
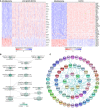
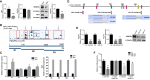
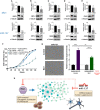
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) and miRNAs are critical gene expression regulators that interact with one another in cooperative and antagonistic fashions. We identified Musashi1 (Msi1) and miR-137 as regulators of a molecular switch between self-renewal and differentiation. Msi1 and miR-137 have opposite expression patterns and functions, and Msi1 is repressed by miR-137. Msi1 is a stem-cell protein implicated in self-renewal while miR-137 functions as a proneuronal differentiation miRNA. In gliomas, miR-137 functions as a tumor suppressor while Msi1 is a prooncogenic factor. We suggest that the balance between Msi1 and miR-137 is a key determinant in cell fate decisions and disruption of this balance could contribute to neurodegenerative diseases and glioma development. Genomic analyses revealed that Msi1 and miR-137 share 141 target genes associated with differentiation, development, and morphogenesis. Initial results pointed out that these two regulators have an opposite impact on the expression of their target genes. Therefore, we propose an antagonistic model in which this network of shared targets could be either repressed by miR-137 or activated by Msi1, leading to different outcomes (self-renewal, proliferation, tumorigenesis).
Keywords: Musashi1; RNA-binding protein; glioblastoma; miR-137; miRNA; neurogenesis.
© 2019 Velasco et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The oncogenic RNA-binding protein Musashi1 is regulated by tumor suppressor miRNAs.RNA Biol. 2011 Sep-Oct;8(5):817-28. doi: 10.4161/rna.8.5.16041. Epub 2011 Sep 1. RNA Biol. 2011. PMID: 21881409
-
Luteolin inhibits Musashi1 binding to RNA and disrupts cancer phenotypes in glioblastoma cells.RNA Biol. 2018;15(11):1420-1432. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2018.1539607. Epub 2018 Nov 18. RNA Biol. 2018. PMID: 30362859 Free PMC article.
-
The oncogenic RNA-binding protein Musashi1 is regulated by HuR via mRNA translation and stability in glioblastoma cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2012 Jan;10(1):143-55. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0208. Mol Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22258704 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular functions of RNA-binding protein, Musashi1, in stem and cancer cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020 May 24;11(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s13287-020-01703-w. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32448364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Musashi1: an RBP with versatile functions in normal and cancer stem cells.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012 Jan 1;17(1):54-64. doi: 10.2741/3915. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012. PMID: 22201732 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-137: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Human Glioma.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Sep 4;21:614-622. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.06.028. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. PMID: 32736290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into Zika Virus Pathogenesis and Potential Therapeutic Strategies.Biomedicines. 2023 Dec 15;11(12):3316. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123316. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Musashi1 Contribution to Glioblastoma Development via Regulation of a Network of DNA Replication, Cell Cycle and Division Genes.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 24;13(7):1494. doi: 10.3390/cancers13071494. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33804958 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Binding Protein COL14A1, TNS1, NUSAP1 and YWHAE Are Valid Biomarkers to Predict Peritoneal Metastasis in Gastric Cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 19;12:830688. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.830688. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35515139 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-binding proteins in tumor progression.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Jul 11;13(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00927-w. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32653017 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
