Heterogeneous translational landscape of the endoplasmic reticulum revealed by ribosome proximity labeling and transcriptome analysis
- PMID: 31004035
- PMCID: PMC6552412
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007996
Heterogeneous translational landscape of the endoplasmic reticulum revealed by ribosome proximity labeling and transcriptome analysis
Abstract
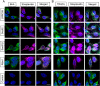
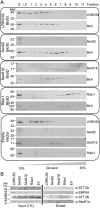
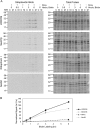
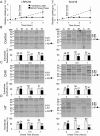
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a nexus for mRNA localization and translation, and recent studies have demonstrated that ER-bound ribosomes also play a transcriptome-wide role in regulating proteome composition. The Sec61 translocon (SEC61) serves as the receptor for ribosomes that translate secretory/integral membrane protein-encoding mRNAs, but whether SEC61 also serves as a translation site for cytosolic protein-encoding mRNAs remains unknown. Here, using a BioID proximity-labeling approach in HEK293T Flp-In cell lines, we examined interactions between ER-resident proteins and ribosomes in vivo Using in vitro analyses, we further focused on bona fide ribosome interactors (i.e. SEC61) and ER proteins (ribophorin I, leucine-rich repeat-containing 59 (LRRC59), and SEC62) previously implicated in associating with ribosomes. We observed labeling of ER-bound ribosomes with the SEC61β and LRRC59 BioID reporters, comparatively modest labeling with the ribophorin I reporter, and no labeling with the SEC62 reporter. A biotin pulse-chase/subcellular fractionation approach to examine ribosome exchange at the SEC61β and LRRC59 sites revealed that, at steady state, ribosomes at these sites comprise both rapid- and slow-exchanging pools. Global translational initiation arrest elicited by the inhibitor harringtonine accelerated SEC61β reporter-labeled ribosome exchange. RNA-Seq analyses of the mRNAs associated with SEC61β- and LRRC59-labeled ribosomes revealed both site-enriched and shared mRNAs and further established that the ER has a transcriptome-wide role in regulating proteome composition. These results provide evidence that ribosomes interact with the ER membrane via multiple modes and suggest regulatory mechanisms that control global proteome composition via ER membrane-bound ribosomes.
Keywords: BioID proximity labeling; RNA-binding protein; Sec translocon; endoplasmic reticulum (ER); mRNA; membrane structure; proteomics; ribosome; ribosome receptor.
© 2019 Hoffman et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures


Similar articles
-
Quantitative Proteomics Links the LRRC59 Interactome to mRNA Translation on the ER Membrane.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020 Nov;19(11):1826-1849. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA120.002228. Epub 2020 Aug 11. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 32788342 Free PMC article.
-
De novo translation initiation on membrane-bound ribosomes as a mechanism for localization of cytosolic protein mRNAs to the endoplasmic reticulum.RNA. 2014 Oct;20(10):1489-98. doi: 10.1261/rna.045526.114. Epub 2014 Aug 20. RNA. 2014. PMID: 25142066 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional roles for the protein translocation machinery in RNA anchoring to the endoplasmic reticulum.J Biol Chem. 2014 Sep 12;289(37):25907-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.580688. Epub 2014 Jul 25. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25063809 Free PMC article.
-
Functions and Mechanisms of the Human Ribosome-Translocon Complex.Subcell Biochem. 2019;93:83-141. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-28151-9_4. Subcell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31939150 Review.
-
In vitro and tissue culture methods for analysis of translation initiation on the endoplasmic reticulum.Methods Enzymol. 2007;431:47-60. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(07)31004-5. Methods Enzymol. 2007. PMID: 17923230 Review.
Cited by
-
Axonal endoplasmic reticulum tubules control local translation via P180/RRBP1-mediated ribosome interactions.Dev Cell. 2024 Aug 19;59(16):2053-2068.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2024.05.005. Epub 2024 May 29. Dev Cell. 2024. PMID: 38815583 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome heterogeneity in stem cells and development.J Cell Biol. 2020 Jun 1;219(6):e202001108. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202001108. J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32330234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative Mass Spectrometry Characterizes Client Spectra of Components for Targeting of Membrane Proteins to and Their Insertion into the Membrane of the Human ER.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 15;24(18):14166. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814166. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
mRNA Targeting, Transport and Local Translation in Eukaryotic Cells: From the Classical View to a Diversity of New Concepts.Mol Biol. 2021;55(4):507-537. doi: 10.1134/S0026893321030080. Epub 2021 May 30. Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34092811 Free PMC article.
-
Chloroplast biogenesis involves spatial coordination of nuclear and organellar gene expression in Chlamydomonas.Plant Physiol. 2024 Sep 2;196(1):112-123. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiae256. Plant Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38709497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fawcett D. W. (1966) An Atlas of Fine Structure: The Cell, Its Organelles, and Inclusions, Reprint Edition, pp. 303–330, WB Saunders Co., Philadelphia, PA
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

