Fingerprinting of Proteins that Mediate Quagga Mussel Adhesion using a De Novo Assembled Foot Transcriptome
- PMID: 31004089
- PMCID: PMC6474901
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-41976-7
Fingerprinting of Proteins that Mediate Quagga Mussel Adhesion using a De Novo Assembled Foot Transcriptome
Abstract
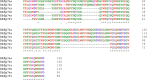
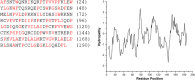
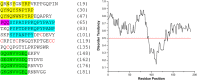
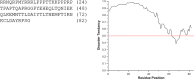
The European freshwater mollusk Dreissena bugensis (quagga mussel), an invasive species to North America, adheres to surfaces underwater via the byssus: a non-living protein 'anchor'. In spite of its importance as a biofouling species, the sequence of the majority of byssal proteins responsible for adhesion are not known, and little genomic data is available. To determine protein sequence information, we utilized next-generation RNA sequencing and de novo assembly to construct a cDNA library of the quagga mussel foot transcriptome, which contains over 200,000 transcripts. Quagga mussel byssal proteins were extracted from freshly induced secretions and analyzed using LC-MS/MS; peptide spectra were matched to the transcriptome to fingerprint the entire protein primary sequences. We present the full sequences of fourteen novel quagga mussel byssal proteins, named Dreissena bugensis foot proteins 4 to 17 (Dbfp4-Dbfp17), and new sequence data for two previously observed byssal proteins Dbfp1 and Dbfp2. Theoretical masses of the newly discovered proteins range from 4.3 kDa to 21.6 kDa. These protein sequences are unique but contain features similar to glue proteins from other species, including a high degree of polymorphism, proteins with repeated peptide motifs, disordered protein structure, and block structures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Karatayev AY, Claudi R, Lucy FE. History of Dreissena Research and the ICAIS Gateway to Aquatic Invasions Science. International Conference on Aquatic Invasive Species. 2010;7(1):1–5.
-
- Hebert PDN, Muncaster BW, Mackie GL. Ecological and Genetic Studies on Dreissena polymorpha (Pallas): a New Mollusc in the Great Lakes. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences. 1989;46(9):1587–1591. doi: 10.1139/f89-202. - DOI
-
- Mills EL, et al. A Review of the Biology and Ecology of the Quagga Mussel (Dreissena bugensis), a Second Species of Freshwater Dreissenid Introduced to North America. Integrative and Comparative Biology. 1996;36(3):271–286.
-
- Ackerman JD, Cottrell CM, Ethier CR, Allen DG. Attachment Strength of Zebra Mussels on Natural, Polymeric, and Metallic Materials. Journal of Environmental Engineering. 1996;122(2):141–148. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(1996)122:2(141). - DOI
-
- Rzepecki LM, Waite JH. The Byssus of the Zebra Mussel, Dreissena polymorpha. I: Morphology and in situ Protein Processing During Maturation. Molecular Marine Biology and Biotechnology. 1993;2(5):255–266. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

