Inhibition of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 preserves cardiac function during regional myocardial ischemia independent of alterations in myocardial substrate utilization
- PMID: 31004234
- PMCID: PMC6616532
- DOI: 10.1007/s00395-019-0733-2
Inhibition of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 preserves cardiac function during regional myocardial ischemia independent of alterations in myocardial substrate utilization
Abstract
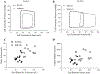
The goal of the present study was to evaluate the effects of SGLT2i on cardiac contractile function, substrate utilization, and efficiency before and during regional myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in normal, metabolically healthy swine. Lean swine received placebo or canagliflozin (300 mg PO) 24 h prior to and the morning of an invasive physiologic study protocol. Hemodynamic and cardiac function measurements were obtained at baseline, during a 30-min complete occlusion of the circumflex coronary artery, and during a 2-h reperfusion period. Blood pressure, heart rate, coronary flow, and myocardial oxygen consumption were unaffected by canagliflozin treatment. Ventricular volumes remained unchanged in controls throughout the protocol. At the onset of ischemia, canagliflozin produced acute large increases in left ventricular end-diastolic and systolic volumes which returned to baseline with reperfusion. Canagliflozin-mediated increases in end-diastolic volume were directly associated with increases in stroke volume and stroke work relative to controls during ischemia. Canagliflozin also increased cardiac work efficiency during ischemia relative to control swine. No differences in myocardial uptake of glucose, lactate, free fatty acids or ketones, were noted between treatment groups at any time. In separate experiments using a longer 60 min coronary occlusion followed by 2 h of reperfusion, canagliflozin increased end-diastolic volume and stroke volume and significantly diminished myocardial infarct size relative to control swine. These data demonstrate that SGLT2i with canagliflozin preserves cardiac contractile function and efficiency during regional myocardial ischemia and provides ischemia protection independent of alterations in myocardial substrate utilization.
Keywords: Cardiac function; Fuel selection; Infarct; Myocardial ischemia; Pig; SGLT2 inhibition.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
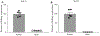
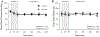

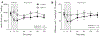
Similar articles
-
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors reduce myocardial infarct size in preclinical animal models of myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury: a meta-analysis.Diabetologia. 2021 Apr;64(4):737-748. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05359-2. Epub 2021 Jan 23. Diabetologia. 2021. PMID: 33483761 Free PMC article.
-
Acute SGLT-2i treatment improves cardiac efficiency during myocardial ischemia independent of Na+/H+ exchanger-1.Int J Cardiol. 2022 Sep 15;363:138-148. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2022.06.054. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Int J Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35753619
-
Acute canagliflozin treatment protects against in vivo myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in non-diabetic male rats and enhances endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation.J Transl Med. 2019 Apr 16;17(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-1881-8. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 30992077 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury under insulin-resistant conditions: SGLT1 but not SGLT2 plays a compensatory protective role in diet-induced obesity.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019 Jul 1;18(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0889-y. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019. PMID: 31262297 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Mechanisms of SGLTi in Ischemic Heart Disease.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2024 Oct;17(5):1018-1035. doi: 10.1007/s12265-024-10513-x. Epub 2024 May 20. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38767796 Review.
Cited by
-
Irisin activates Opa1-induced mitophagy to protect cardiomyocytes against apoptosis following myocardial infarction.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Mar 10;12(5):4474-4488. doi: 10.18632/aging.102899. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32155590 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological basis of the cardiological benefits of SGLT-2 inhibitors: a narrative review.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023 Jun 30;22(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12933-023-01855-y. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023. PMID: 37391739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidized LDL Disrupts Metabolism and Inhibits Macrophage Survival by Activating a miR-9/Drp1/Mitochondrial Fission Signaling Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Nov 1;2020:8848930. doi: 10.1155/2020/8848930. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023 Oct 11;2023:9763019. doi: 10.1155/2023/9763019. PMID: 33204400 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors reduce myocardial infarct size in preclinical animal models of myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury: a meta-analysis.Diabetologia. 2021 Apr;64(4):737-748. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05359-2. Epub 2021 Jan 23. Diabetologia. 2021. PMID: 33483761 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic high-rate pacing induces heart failure with preserved ejection fraction-like phenotype in Ossabaw swine.Basic Res Cardiol. 2022 Oct 12;117(1):50. doi: 10.1007/s00395-022-00958-z. Basic Res Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 36222894 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreadou I, Efentakis P, Balafas E, Togliatto G, Davos CH, Varela A, Dimitriou CA, Nikolaou PE, Maratou E, Lambadiari V, Ikonomidis I, Kostomitsopoulos N, Brizzi MF, Dimitriadis G, Iliodromitis EK (2017) Empagliflozin limits myocardial infarction in vivo and cell death in vitro: role of STAT3, mitochondria, and redox aspects. Front Physiol 8:1077 10.3389/fphys.2017.01077 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

