Manual for clinical language tractography
- PMID: 31004240
- PMCID: PMC6525736
- DOI: 10.1007/s00701-019-03899-0
Manual for clinical language tractography
Abstract
Background: We introduce a user-friendly, standardized protocol for tractography of the major language fiber bundles.
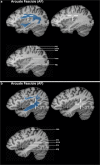
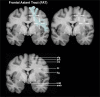
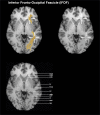
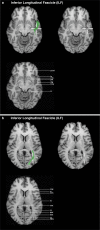
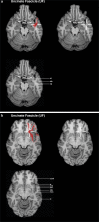
Method: The introduced method uses dMRI images for tractography whereas the ROI definition is based on structural T1 MPRAGE MRI templates, without normalization to MNI space. ROIs for five language-relevant fiber bundles were visualized on an axial, coronal, or sagittal view of T1 MPRAGE images. The ROIs were defined based upon the tracts' obligatory pathways, derived from literature and own experiences in peritumoral tractography.
Results: The resulting guideline was evaluated for each fiber bundle in ten healthy subjects and ten patients by one expert and three raters. Overall, 300 ROIs were evaluated and compared. The targeted language fiber bundles could be tracked in 88% of the ROI pairs, based on the raters' result blinded ROI placements. The evaluation indicated that the precision of the ROIs did not relate to the varying experience of the raters.
Conclusions: Our guideline introduces a standardized language tractography method for routine preoperative workup and for research contexts. The ROI placement guideline based on easy-to-identify anatomical landmarks proved to be user-friendly and accurate, also in inexperienced test persons.
Keywords: Brain tumor surgery; Diffusion tensor imaging; Language; Neuroanatomy; Tractography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Language pathway tracking: comparing nTMS-based DTI fiber tracking with a cubic ROIs-based protocol.J Neurosurg. 2017 Mar;126(3):1006-1014. doi: 10.3171/2016.2.JNS152382. Epub 2016 May 27. J Neurosurg. 2017. PMID: 27231977
-
Functional MRI vs. navigated TMS to optimize M1 seed volume delineation for DTI tractography. A prospective study in patients with brain tumours adjacent to the corticospinal tract.Neuroimage Clin. 2016 Nov 23;13:297-309. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2016.11.022. eCollection 2017. Neuroimage Clin. 2016. PMID: 28050345 Free PMC article.
-
A majority rule approach for region-of-interest-guided streamline fiber tractography.Brain Imaging Behav. 2016 Dec;10(4):1137-1147. doi: 10.1007/s11682-015-9474-5. Brain Imaging Behav. 2016. PMID: 26572144 Free PMC article.
-
Merits and Limits of Tractography Techniques for the Uninitiated.Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg. 2016;(43):37-60. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-21359-0_2. Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26508405 Review.
-
Common misconceptions, hidden biases and modern challenges of dMRI tractography.J Neural Eng. 2020 Feb 18;17(1):011001. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ab6aad. J Neural Eng. 2020. PMID: 31931484 Review.
Cited by
-
Preoperative Repetitive Navigated TMS and Functional White Matter Tractography in a Bilingual Patient with a Brain Tumor in Wernike Area.Brain Sci. 2021 Apr 28;11(5):557. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11050557. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 33924964 Free PMC article.
-
The Relevant Role of Navigated Tractography in Speech Eloquent Area Glioma Surgery: Single Center Experience.Brain Sci. 2021 Oct 28;11(11):1436. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11111436. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 34827434 Free PMC article.
-
Structural connectivity in ventral language pathways characterizes non-verbal autism.Brain Struct Funct. 2022 Jun;227(5):1817-1829. doi: 10.1007/s00429-022-02474-1. Epub 2022 Mar 14. Brain Struct Funct. 2022. PMID: 35286477 Free PMC article.
-
Function-guided differences of arcuate fascicle and inferior fronto-occipital fascicle tractography as diagnostic indicators for surgical risk stratification.Brain Struct Funct. 2024 Dec;229(9):2219-2235. doi: 10.1007/s00429-024-02787-3. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Brain Struct Funct. 2024. PMID: 38597941 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping action naming in patients with gliomas: The influence of transitivity.Neuroimage Rep. 2023 Sep 21;3(4):100184. doi: 10.1016/j.ynirp.2023.100184. eCollection 2023 Dec. Neuroimage Rep. 2023. PMID: 40567822 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

