Intravenous Oxycodone Versus Other Intravenous Strong Opioids for Acute Postoperative Pain Control: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 31004317
- PMCID: PMC6514019
- DOI: 10.1007/s40122-019-0122-4
Intravenous Oxycodone Versus Other Intravenous Strong Opioids for Acute Postoperative Pain Control: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
Introduction: Optimal pain management is crucial to the postoperative recovery process. We aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of intravenous oxycodone with intravenous fentanyl, morphine, sufentanil, pethidine, and hydromorphone for acute postoperative pain.
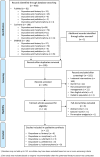
Methods: A systematic literature search of PubMed, Cochrane Library, and EMBASE databases was performed for randomized controlled trials published from 2008 through 2017 (inclusive) that evaluated the acute postoperative analgesic efficacy of intravenous oxycodone against fentanyl, morphine, sufentanil, pethidine, and hydromorphone in adult patients (age ≥ 18 years). Outcomes examined included analgesic consumption, pain intensity levels, side effects, and patient satisfaction.
Results: Eleven studies were included in the review; six compared oxycodone with fentanyl, two compared oxycodone with morphine, and three compared oxycodone with sufentanil. There were no eligible studies comparing oxycodone with pethidine or hydromorphone. Overall, analgesic consumption was lower with oxycodone than with fentanyl or sufentanil. Oxycodone exhibited better analgesic efficacy than fentanyl and sufentanil, and comparable analgesic efficacy to morphine. In terms of safety, there was a tendency towards more side effects with oxycodone than with fentanyl, but the incidence of side effects with oxycodone was comparable to morphine and sufentanil. Where patient satisfaction was evaluated, higher satisfaction levels were observed with oxycodone than with sufentanil and comparable satisfaction was noted when comparing oxycodone with fentanyl. Patient satisfaction was not evaluated in the studies comparing oxycodone with morphine.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that intravenous oxycodone provides better analgesic efficacy than fentanyl and sufentanil, and comparable efficacy to morphine with less adverse events such as sedation. No studies comparing intravenous oxycodone with pethidine or hydromorphone were identified in this review. Better alignment of study methodologies for future research in this area is recommended to provide the best evidence base for a meta-analysis.
Funding: Mundipharma Singapore Holding Pte Ltd, Singapore.
Keywords: Acute postoperative pain; Fentanyl; Hydromorphone; Morphine; Oxycodone; Pethidine; Sufentanil.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxycodone versus other opioid analgesics after laparoscopic surgery: a meta-analysis.Eur J Med Res. 2021 Jan 9;26(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s40001-020-00463-w. Eur J Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33422129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Efficacy of Oxycodone Hydrochloride for Patient-controlled Intravenous Analgesia after General Surgery].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2020 Feb 28;42(1):91-95. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.11141. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 32131946 Chinese.
-
Opioids and the management of chronic severe pain in the elderly: consensus statement of an International Expert Panel with focus on the six clinically most often used World Health Organization Step III opioids (buprenorphine, fentanyl, hydromorphone, methadone, morphine, oxycodone).Pain Pract. 2008 Jul-Aug;8(4):287-313. doi: 10.1111/j.1533-2500.2008.00204.x. Epub 2008 May 23. Pain Pract. 2008. PMID: 18503626
-
Comparison of oxycodone and sufentanil in patient-controlled intravenous analgesia for postoperative patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Chin Med J (Engl). 2023 Jan 5;136(1):45-52. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002259. Chin Med J (Engl). 2023. PMID: 36878002 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-Controlled Intravenous Analgesia for Advanced Cancer Patients with Pain: A Retrospective Series Study.Pain Res Manag. 2018 Apr 4;2018:7323581. doi: 10.1155/2018/7323581. eCollection 2018. Pain Res Manag. 2018. PMID: 29849846 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Oxycodone vs the Combination of Fentanyl and Remifentanil for General Anesthesia in Laparoscopic Uterine Myomas Surgery: A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Study.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Jun 9;19:4979-4990. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S524102. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40521011 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pain Management During the COVID-19 Pandemic.Pain Ther. 2020 Dec;9(2):453-466. doi: 10.1007/s40122-020-00190-4. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Pain Ther. 2020. PMID: 32840756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of fentanyl, oxycodone, and butorphanol on gastrointestinal function in patients undergoing laparoscopic hysterectomy: a prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2022 Feb 24;22(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01594-9. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022. PMID: 35209847 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Oxycodone in the Opioid Epidemic: High 'Liking', 'Wanting', and Abuse Liability.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Jul;41(5):899-926. doi: 10.1007/s10571-020-01013-y. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 33245509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of an opioid-free care pathway vs. opioid-based standard care on postoperative pain and postoperative quality of recovery after laparoscopic bariatric surgery: A multicentre randomised controlled trial.Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2025 Aug 1;42(8):714-726. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000002193. Epub 2025 May 14. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 40371564 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Apfelbaum JL, Chen C, Mehta SS, Gan TJ. Postoperative pain experience: results from a national survey suggest postoperative pain continues to be undermanaged. Anesth Analg. 2003;97(2):534–540. - PubMed
-
- Rawal N. Current issues in postoperative pain management. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2016;33(3):160–171. - PubMed
-
- Montgomery R, McNamara SA. Multimodal pain management for enhanced recovery: reinforcing the shift from traditional pathways through nurse-led interventions. AORN J. 2016;104(6S):S9–S16. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources