Neural substrates of self- and external-preoccupation: A voxel-based morphometry study
- PMID: 31004413
- PMCID: PMC6576210
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.1267
Neural substrates of self- and external-preoccupation: A voxel-based morphometry study
Abstract
Introduction: Self- and external-preoccupation have been linked to psychopathological states. The neural substrates underlying self- and external-preoccupation remain unclear. In the present study, we aim to provide insight into the information-processing mechanisms associated with self- and external-preoccupation at the structural level.
Methods: To investigate the neural substrates of self- and external-preoccupation, we acquired high-resolution T1-weighted structural images and Preoccupation Scale scores from 1,122 young subjects. Associations between regional gray matter volume (rGMV) and Preoccupation Scale subscores for self- and external-preoccupation were estimated using voxel-based morphometry.
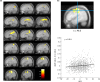
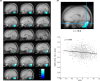
Results: Significant positive associations between self-preoccupation and rGMV were observed in widespread brain areas such as the bilateral precuneus and posterior cingulate gyri, structures known to be associated with self-triggered self-reference during rest. Significant negative associations between external-preoccupation and rGMV were observed only in the bilateral cerebellum, regions known to be associated with behavioral addiction, sustained attention, and reward system.
Conclusion: Our results reveal distinct neural substrates for self- and external-preoccupation at the structural level.
Keywords: Preoccupation Scale; cerebellum; gray matter volume; magnetic resonance imaging; posterior cingulate cortex; precuneus.
© 2019 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Costa, P. T. , & MacCrae, R. R. (1992). Revised NEO personality inventory (NEO PI‐R) and NEO five‐factor inventory (NEO FFI): Professional manual. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

