ORCA: a comprehensive bioinformatics container environment for education and research
- PMID: 31004474
- PMCID: PMC6821186
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz278
ORCA: a comprehensive bioinformatics container environment for education and research
Abstract
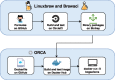
Summary: The ORCA bioinformatics environment is a Docker image that contains hundreds of bioinformatics tools and their dependencies. The ORCA image and accompanying server infrastructure provide a comprehensive bioinformatics environment for education and research. The ORCA environment on a server is implemented using Docker containers, but without requiring users to interact directly with Docker, suitable for novices who may not yet have familiarity with managing containers. ORCA has been used successfully to provide a private bioinformatics environment to external collaborators at a large genome institute, for teaching an undergraduate class on bioinformatics targeted at biologists, and to provide a ready-to-go bioinformatics suite for a hackathon. Using ORCA eliminates time that would be spent debugging software installation issues, so that time may be better spent on education and research.
Availability and implementation: The ORCA Docker image is available at https://hub.docker.com/r/bcgsc/orca/. The source code of ORCA is available at https://github.com/bcgsc/orca under the MIT license.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- Jackman S,D., Birol I. (2016) Linuxbrew and Homebrew for cross-platform package management [v1; not peer reviewed]. F1000Res., 5(ISCB Comm J), 1795 (poster).

