Inhibition of Brd4 alleviates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress by blocking FoxO4-mediated oxidative stress
- PMID: 31004990
- PMCID: PMC6475721
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101195
Inhibition of Brd4 alleviates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury-induced apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress by blocking FoxO4-mediated oxidative stress
Abstract
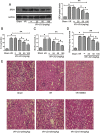
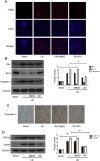
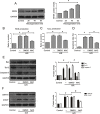
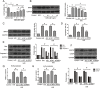
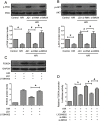
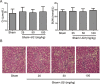
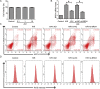
Ischemia/reperfusion injury (I/R) is one of the leading causes of acute kidney injury (AKI) that typically occurs in renal surgeries. However, renal I/R still currently lacks effective therapeutic targets. In this study, we proved that inhibition of Brd4 with its selective inhibitor, JQ1, could exert a protective role in renal I/R injury in mice. Inhibiting Brd4 with either JQ1 or genetic knockdown resulted in reduction of endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS)-associated protein and proapoptotic protein expression both in I/R-induced injury and hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) stimulation in HK-2 cells. H/R-induced apoptosis and ERS depended on oxidative stress in vitro. Moreover, FoxO4, which is involved in the generation of hydrogen peroxide, was up-regulated during H/R stimulation-mediated apoptosis and ERS, and this upregulation could be abolished by Brd4 inhibition. Consistently, FoxO4-mediated ROS generation was attenuated upon inhibition of Brd4 with JQ1 or siRNA against Brd4. Further, the transcriptional activity of FoxO4 was suppressed by PI3K and AKT phosphorylation, which are upstream signals of FoxO4 expression, and were enhanced by Brd4 both in vivo and in vitro. In conclusion, our results proved that Brd4 inhibition blocked renal apoptotic and ERS protein expression by preventing FoxO4-dependent ROS generation through the PI3K/AKT pathway, indicating that Brd4 could be a potential therapeutic target for renal I/R injury.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Brd4; ERS; Oxidative stress; Renal I/R injury.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Nobiletin alleviates ischemia/reperfusion injury in the kidney by activating PI3K/AKT pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Dec;22(6):4655-4662. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11554. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 33173956 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin32 plays a crucial role in ROS-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress apoptosis signaling pathway in ischemia reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury.J Transl Med. 2018 May 4;16(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1493-8. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29728112 Free PMC article.
-
Brd4 inhibition attenuates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced fibrosis by blocking TGF-β-mediated Nox4 expression.Redox Biol. 2017 Apr;11:390-402. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2016.12.031. Epub 2016 Dec 30. Redox Biol. 2017. PMID: 28063381 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K/AKT pathway: A potential therapeutic target in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 5;998:177505. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177505. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40118329 Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Hydrogen Sulfide in Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury.Biomolecules. 2024 Jun 22;14(7):740. doi: 10.3390/biom14070740. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062455 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Naringenin Alleviates Renal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Suppressing ER Stress-Induced Pyroptosis and Apoptosis through Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Oct 10;2022:5992436. doi: 10.1155/2022/5992436. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36262286 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of FOXO4 protects against OGD/R‑induced cerebral microvascular endothelial cell injury and regulates the AMPK/Nrf2/HO‑1 pathway through transcriptional activation of CTRP6.Exp Ther Med. 2024 Jan 9;27(3):94. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12382. eCollection 2024 Mar. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 38313581 Free PMC article.
-
Remote liver ischemic preconditioning protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 in mice.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 19;19(8):e0308977. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308977. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39159207 Free PMC article.
-
Breast Cancer Exosome-Derived miR-425-5p Induces Cancer-Associated Fibroblast-Like Properties in Human Mammary Fibroblasts by TGFβ1/ROS Signaling Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Nov 30;2022:5266627. doi: 10.1155/2022/5266627. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023 Jun 21;2023:9857678. doi: 10.1155/2023/9857678. PMID: 36506936 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
β-Cryptoxanthin Maintains Mitochondrial Function by Promoting NRF2 Nuclear Translocation to Inhibit Oxidative Stress-Induced Senescence in HK-2 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 14;24(4):3851. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043851. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Devarajan P. Update on mechanisms of ischemic acute kidney injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006;17(6):1503–1520. - PubMed
-
- Ikeda M., Prachasilchai W., Burne-Taney M.J., Rabb H., Yokota-Ikeda N. Ischemic acute tubular necrosis models and drug discovery: a focus on cellular inflammation. Drug Discov. Today. 2006;11(7–8):364–370. - PubMed
-
- Li B., Haridas B., Jackson A.R., Cortado H., Mayne N., Kohnken R., Bolon B., Mchugh K.M., Schwaderer A.L., Spencer J.D., Ching C.B., Hains D.S., Justice S.S., Partida-Sanchez S., Becknell B. Inflammation drives renal scarring in experimental pyelonephritis. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2017;312(1):F43–F53. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

