Prognostic Implications of Blunted Feature-Tracking Global Longitudinal Strain During Vasodilator Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Stress Imaging
- PMID: 31005520
- PMCID: PMC6745296
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2019.03.002
Prognostic Implications of Blunted Feature-Tracking Global Longitudinal Strain During Vasodilator Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Stress Imaging
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to determine the prognostic value of feature-tracking global longitudinal strain (GLS) measured during vasodilator stress cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging.
Background: Prior studies have suggested that blunted myocardial strain during dobutamine stress echocardiography may be associated with adverse prognosis. Recent developments in CMR feature-tracking techniques now allow assessment of strain in clinical practice using standard cine images without specialized pulse sequences or complex post-processing. Whether feature-tracking GLS measured during vasodilator stress provides independent and incremental prognostic data is unclear.
Methods: Consecutive patients undergoing stress perfusion CMR were prospectively enrolled (n = 535). Feature-tracking stress GLS was measured immediately after regadenoson perfusion. Patients were followed for major adverse cardiac events (MACE): death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, heart failure hospitalization, sustained ventricular tachycardia, and late revascularization. Cox proportional hazards regression modeling was used to examine the association between stress GLS and MACE. The incremental prognostic value of stress GLS was assessed in nested models.
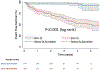
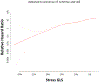
Results: Over a median follow-up of 1.5 years, 82 patients experienced MACE. By Kaplan-Meier analysis, patients with stress GLS ≥ median (-19%) had significantly reduced event-free survival compared with those with stress GLS < median (log-rank p < 0.001). Stress GLS was significantly associated with risk of MACE after adjustment for clinical and imaging risk factors including ischemia, ejection fraction, and late gadolinium enhancement (hazard ratio: 1.267; p < 0.001). Addition of stress GLS into a model with clinical and imaging predictors resulted in significant increase in the C-index (from 0.80 to 0.85; p = 0.031) and a continuous net reclassification improvement of 0.898 (95% confidence interval: 0.565 to 1.124).
Conclusions: Feature-tracking stress GLS measured during vasodilator stress CMR is an independent predictor of MACE in patients with known or suspected coronary artery disease, incremental to common clinical and imaging risk factors. These findings suggest a role for feature-tracking derived stress GLS in identifying patients at highest risk of adverse events following stress CMR.
Keywords: cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; coronary artery disease; global longitudinal strain; prognosis; stress testing.
Copyright © 2020 American College of Cardiology Foundation. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Strain for Stress Testing: Is it a Featuring or Supporting Role in Cardiac Magnetic Resonance?JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020 Jan;13(1 Pt 1):66-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2019.04.006. Epub 2019 May 15. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020. PMID: 31103585 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Global Coronary Flow Reserve Measured During Stress Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging Is an Independent Predictor of Adverse Cardiovascular Events.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 Aug;12(8 Pt 2):1686-1695. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.08.018. Epub 2018 Nov 5. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30409558
-
Feature-Tracking Global Longitudinal Strain Predicts Death in a Multicenter Population of Patients With Ischemic and Nonischemic Dilated Cardiomyopathy Incremental to Ejection Fraction and Late Gadolinium Enhancement.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018 Oct;11(10):1419-1429. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2017.10.024. Epub 2018 Jan 17. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29361479 Free PMC article.
-
Feature-Tracking Global Longitudinal Strain Predicts Mortality in Patients With Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Multicenter Study.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020 Apr;13(4):940-947. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2019.10.004. Epub 2019 Nov 11. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020. PMID: 31727563 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of stress cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in patients with known or suspected coronary artery disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Aug 27;62(9):826-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.03.080. Epub 2013 May 30. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23727209 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic impact of MRI-derived feature tracking myocardial strain in patients with non-ischaemic dilated cardiomyopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Radiol. 2024 May;79(5):e702-e714. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2023.12.029. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Clin Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38402086
Cited by
-
CMR for myocardial characterization in ischemic heart disease: state-of-the-art and future developments.Eur Radiol Exp. 2021 Mar 25;5(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s41747-021-00208-2. Eur Radiol Exp. 2021. PMID: 33763757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Quantification of Structure-Function Relationships in Heart Failure.Heart Fail Clin. 2021 Jan;17(1):9-24. doi: 10.1016/j.hfc.2020.08.001. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Heart Fail Clin. 2021. PMID: 33220890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fast-Strain Encoded Cardiac Magnetic Resonance During Vasodilator Perfusion Stress Testing.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Nov 17;8:765961. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.765961. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34869679 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of myocardial deformation on risk prediction in patients following acute myocardial infarction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Aug 10;10:1199936. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1199936. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37636296 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Feature Tracking Global Longitudinal Strain and Prognosis After Heart Transplantation.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020 Sep;13(9):1934-1942. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2020.04.004. Epub 2020 Jun 17. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32563650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bjork Ingul C, Rozis E, Slordahl SA, Marwick TH. Incremental value of strain rate imaging to wall motion analysis for prediction of outcome in patients undergoing dobutamine stress echocardiography. Circulation 2007;115:1252–9. - PubMed
-
- Pedrizzetti G, Claus P, Kilner PJ, Nagel E. Principles of cardiovascular magnetic resonance feature tracking and echocardiographic speckle tracking for informed clinical use. Journal of cardiovascular magnetic resonance : official journal of the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 2016; 18:51. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Romano S, Judd RM, Kim RJ et al. Feature-Tracking Global Longitudinal Strain Predicts Death in a Multicenter Population of Patients With Ischemic and Nonischemic Dilated Cardiomyopathy Incremental to Ejection Fraction and Late Gadolinium Enhancement. JACC Cardiovascular imaging 2018;11:1419–1429. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Garg P, Aziz R, Al Musa T et al. Effects of hyperaemia on left ventricular longitudinal strain in patients with suspected coronary artery disease : A first-pass stress perfusion cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging study. Netherlands heart journal : monthly journal of the Netherlands Society of Cardiology and the Netherlands Heart Foundation 2018;26:85–93. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

