Treatment of Type II Collagen-Induced Rat Rheumatoid Arthritis Model by Interleukin 10 (IL10)-Mesenchymal Stem Cells (BMSCs)
- PMID: 31005957
- PMCID: PMC6489530
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.911184
Treatment of Type II Collagen-Induced Rat Rheumatoid Arthritis Model by Interleukin 10 (IL10)-Mesenchymal Stem Cells (BMSCs)
Abstract
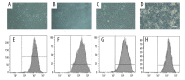
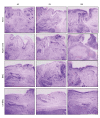
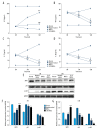
BACKGROUND Rheumatoid arthritis model (CIA) rats were treated by tail vein injection of IL-10-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) to investigate its feasibility and intrinsic molecular mechanism. MATERIAL AND METHODS The CIA rat model was established by induction type II collagen, and IL-10-modified BMSCs was established by transfecting BMSCs with adenovirus. IL-10-modified BMSCs were used to treat the CIA rats. The therapeutic effect was evaluated by measuring the changes in body weight, ankle swelling, and forced swimming time, as well as observation of synovial hyperplasia and cartilage tissue repair by HE staining. Western blot analysis and ELISA were used to detect gene expression. RESULTS After 4 weeks and 8 weeks of treatment with IL10-BMSCs, the body weight, swelling value, resting time, and forced swimming struggle time of CIA rats were significantly higher than those of BMSCs-treated and -untreated CIA rats (P<0.05). Compared to BMSCs-treated CIA model rats, after treatment with IL10-BMSCs, the repair rate of osteoarticular cartilage was higher and the inhibition of synovial proliferation was better, and serum IL-17, IL-1ß, and TNF-alpha levels were lower. We found that the protein level of SIRT1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells was lower, the protein level in spleen was higher, and phosphorylation of p65 protein in peripheral blood mononuclear cells was reduced. CONCLUSIONS The efficacy of tail vein injection of IL-10-modified BMSCs in treatment of CIA rats was superior to that of BMSCs alone, which may be related to the more pronounced suppression of IL-10-modified BMSCs in peripheral blood inflammation and spleen immune response.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Transplantation of IL-1β siRNA-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates type II collagen-induced rheumatoid arthritis in rats.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Feb;23(2):139. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.11062. Epub 2021 Dec 14. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35069820 Free PMC article.
-
Kirenol exerts a potent anti-arthritic effect in collagen-induced arthritis by modifying the T cells balance.Phytomedicine. 2012 Jul 15;19(10):882-9. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2012.04.010. Epub 2012 Jun 4. Phytomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22673798
-
Protection against cartilage and bone destruction by systemic interleukin-4 treatment in established murine type II collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Res. 1999;1(1):81-91. doi: 10.1186/ar14. Epub 1999 Oct 26. Arthritis Res. 1999. PMID: 11056663 Free PMC article.
-
Extract of the dried heartwood of Caesalpinia sappan L. attenuates collagen-induced arthritis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Jun 14;136(1):271-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.04.061. Epub 2011 Apr 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21557995
-
Pathogenesis of Collagen-Induced Arthritis: Role of Immune Cells with Associated Cytokines and Antibodies, Comparison with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Folia Biol (Praha). 2023;69(2):41-49. doi: 10.14712/fb2023069020041. Folia Biol (Praha). 2023. PMID: 38063000 Review.
Cited by
-
Salvianolic acid B combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells piggybacked on HAMA hydrogel re-transplantation improves intervertebral disc degeneration.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Sep 27;10:950625. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.950625. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36237221 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-based therapy for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: An update on preclinical studies.EBioMedicine. 2021 Jul;69:103427. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103427. Epub 2021 Jun 20. EBioMedicine. 2021. PMID: 34161884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lithium Chloride-Releasing 3D Printed Scaffold for Enhanced Cartilage Regeneration.Med Sci Monit. 2019 May 31;25:4041-4050. doi: 10.12659/MSM.916918. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31147532 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of microRNA-515-5p on the Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4)/JNK Signaling Pathway and WNT1-Inducible-Signaling Pathway Protein 1 (WISP-1) Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synovial (RAFLS) Cells Following Treatment with Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-kappa-B Ligand (RANKL).Med Sci Monit. 2020 May 3;26:e920611. doi: 10.12659/MSM.920611. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32361708 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on autoimmune diseases.World J Stem Cells. 2025 Jul 26;17(7):107202. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i7.107202. World J Stem Cells. 2025. PMID: 40740529 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kyburz D, Finckh A. The importance of early treatment for the prognosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Swiss Med Wkly. 2013;143:w13865. - PubMed
-
- Smolen JS, Burmester G-R, Combe B, et al. Head-to-head comparison of certolizumab pegol versus adalimumab in rheumatoid arthritis: 2-year efficacy and safety results from the randomised EXXELERATE study. Lancet. 2016;388:2763–74. - PubMed
-
- Singh JA, Saag KG, Bridges SL, Jr, et al. 2015 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2016;68:1–25. - PubMed
-
- Lequerré T, Avenel G, Vittecoq O. [Therapeutic update in rheumatoid arthritis]. La Revue De Medecine Interne. 2013;34:754–62. - PubMed
-
- Mcinnes IB, O’Dell JR. State-of-the-art: rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:1898–906. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

