Flavonoids: Broad Spectrum Agents on Chronic Inflammation
- PMID: 31006180
- PMCID: PMC6513185
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2019.034
Flavonoids: Broad Spectrum Agents on Chronic Inflammation
Abstract
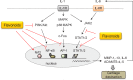
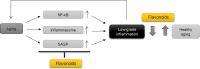
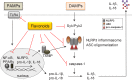
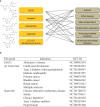
Flavonoids are major plant constituents with numerous biological/pharmacological actions both in vitro and in vivo. Of these actions, their anti-inflammatory action is prominent. They can regulate transcription of many proinflammatory genes such as cyclooxygenase- 2/inducible nitric oxide synthase and many cytokines/chemokines. Recent studies have demonstrated that certain flavonoid derivatives can affect pathways of inflammasome activation and autophagy. Certain flavonoids can also accelerate the resolution phase of inflammation, leading to avoiding chronic inflammatory stimuli. All these pharmacological actions with newly emerging activities render flavonoids to be potential therapeutics for chronic inflammatory disorders including arthritic inflammation, meta-inflammation, and inflammaging. Recent findings of flavonoids are summarized and future perspectives are presented in this review.
Keywords: Chronic inflammation; Flavonoid; Inflammaging; Meta-inflammation; Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alimbetov D, Davis T, Brook AJ, Cox LS, Faragher RG, Nurgozhin T, Zhumadilov Z, Kipling D. Suppression of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) in human fibroblasts using small molecule inhibitors of p38 MAP kinase and MK2. Biogerontology. 2016;17:305–315. doi: 10.1007/s10522-015-9610-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

