Appropriate treatment modality for solitary small hepatocellular carcinoma: Radiofrequency ablation vs. resection vs. transplantation?
- PMID: 31006225
- PMCID: PMC6933127
- DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2018.0096
Appropriate treatment modality for solitary small hepatocellular carcinoma: Radiofrequency ablation vs. resection vs. transplantation?
Abstract
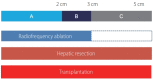
There has been controversy regarding the first-line treatment modality for the patients who have small solitary hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); radiofrequency ablation (RFA) or percutaneous ethanol injection (PEI), surgical hepatic resection (HR) and liver transplantation (LT). For selection of treatment modality of HCC, it should be considered of hepatic reservoir function as well as the tumor stage. If the liver function is good enough, HR may be the first choice regardless of the tumor size. However, recent studies comparing RFA with resection showed comparable outcome and similar survival rates. RFA, HR and LT provide good outcome for patients who have small HCCs. RFA would be desired in patients who have below 3.0 cm in size and low alpha-fetoprotein (<200 ng/mL). However, in small HCC with high tumor marker, HR should be considered. Better patient selection for the 'resection first' approach and early detection of recurrence can achieve better outcomes of the salvage LT strategy. Another benefit of resection first strategy is that it make possible to do enlist of LT for patients before recurrence at high risk of HCC recurrence after resection on the basis of pathologic aggressiveness, microvascular invasion and/or satellites nodule. They should be applied appropriately according to the tumor size, location, tumor markers and underlying liver parenchymal disease.
Keywords: Hepatectomy; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Liver transplantation; Radiofrequency ablation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Outcomes of radiofrequency ablation as first-line therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma less than 3 cm in potentially transplantable patients.J Hepatol. 2019 May;70(5):866-873. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.12.027. Epub 2019 Jan 5. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30615906
-
Combined percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and ethanol injection versus hepatic resection for 2.1-5.0 cm solitary hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective comparative multicentre study.Eur Radiol. 2018 Sep;28(9):3651-3660. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5371-9. Epub 2018 Mar 29. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29600474
-
Cost-effectiveness of hepatic resection versus percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for early hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2013 Aug;59(2):300-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.04.009. Epub 2013 Apr 18. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23603669
-
Meta-analysis of the therapeutic effect of hepatectomy versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2010 Jun;20(3):130-40. doi: 10.1097/SLE.0b013e3181d823df. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2010. PMID: 20551807 Review.
-
Liver resection versus radiofrequency ablation for solitary small hepatocellular carcinoma measuring ≤3 cm: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2025 May 1;111(5):3456-3466. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002302. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 39998503 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Recent progress in treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Sep 1;10(9):2993-3036. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33042631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of preoperative transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) on postoperative long-term survival in patients with nonsmall hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score matching analysis.BMC Cancer. 2024 Feb 9;24(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-11978-4. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38336712 Free PMC article.
-
Prognosis of Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Comparison between Trans-Arterial Chemoembolization and Radiofrequency Ablation.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 5;12(9):2527. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092527. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32899584 Free PMC article.
-
Appraisal of Long-Term Outcomes of Liver-Directed Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Major Portal Vein Invasion.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2020 Dec 17;7:403-412. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S276528. eCollection 2020. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2020. PMID: 33365287 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a model to predict the risk of distant metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma: a real-world retrospective study.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Dec;149(18):16489-16499. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05361-2. Epub 2023 Sep 15. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37712961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang G, Chen X, Lau WY, Shen F, Wang RY, Yuan SX, et al. Quality of life after surgical resection compared with radiofrequency ablation for small hepatocellular carcinomas. Br J Surg. 2014;101:1006–1015. - PubMed
-
- Hasegawa K, Kokudo N, Makuuchi M, Izumi N, Ichida T, Kudo M, et al. Comparison of resection and ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a cohort study based on a Japanese nationwide survey. J Hepatol. 2013;58:724–729. - PubMed
-
- Kutlu OC, Chan JA, Aloia TA, Chun YS, Kaseb AO, Passot G, et al. Comparative effectiveness of first-line radiofrequency ablation versus surgical resection and transplantation for patients with early hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2017;123:1817–1827. - PubMed
-
- Kim GA, Shim JH, Kim MJ, Kim SY, Won HJ, Shin YM, et al. Radiofrequency ablation as an alternative to hepatic resection for single small hepatocellular carcinomas. Br J Surg. 2016;103:126–135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

