TEX264 Is an Endoplasmic Reticulum-Resident ATG8-Interacting Protein Critical for ER Remodeling during Nutrient Stress
- PMID: 31006537
- PMCID: PMC6747008
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.03.034
TEX264 Is an Endoplasmic Reticulum-Resident ATG8-Interacting Protein Critical for ER Remodeling during Nutrient Stress
Abstract
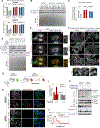
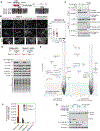
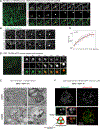
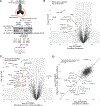
Cells respond to nutrient stress by trafficking cytosolic contents to lysosomes for degradation via macroautophagy. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) serves as an initiation site for autophagosomes and is also remodeled in response to nutrient stress through ER-phagy, a form of selective autophagy. Quantitative proteome analysis during nutrient stress identified an unstudied single-pass transmembrane ER protein, TEX264, as an ER-phagy receptor. TEX264 uses an LC3-interacting region (LIR) to traffic into ATG8-positive puncta that often initiate from three-way ER tubule junctions and subsequently fuse with lysosomes. Interaction and proximity biotinylation proteomics identified a cohort of autophagy regulatory proteins and cargo adaptors located near TEX264 in an LIR-dependent manner. Global proteomics and ER-phagy flux analysis revealed the stabilization of a cohort of ER proteins in TEX264-/- cells during nutrient stress. This work reveals TEX264 as an unrecognized ER-phagy receptor that acts independently of other candidate ER-phagy receptors to remodel the ER during nutrient stress.
Keywords: ER-phagy; TEX264; selective autophagy.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
J.W.H. is a consultant and founder of Rheostat Therapeutics and a consultant for X-Chem Inc.
Figures


Comment in
-
Picky Eating at the ER-phagy Buffet.Trends Biochem Sci. 2019 Sep;44(9):731-733. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2019.05.003. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Trends Biochem Sci. 2019. PMID: 31176531
-
TEX264 is a major receptor for mammalian reticulophagy.Autophagy. 2019 Oct;15(10):1677-1681. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1646540. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Autophagy. 2019. PMID: 31362563 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anantharaman V, and Aravind L (2004). The SHS2 module is a common structural theme in functionally diverse protein groups, like Rpb7p, FtsA, GyrI, and MTH1598/TM1083 superfamilies. Proteins 56, 795–807. - PubMed
-
- Fumagalli F, Noack J, Bergmann TJ, Cebollero E, Pisoni GB, Fasana E, Fregno I, Galli C, Loi M, Solda T, et al. (2016). Translocon component Sec62 acts in endoplasmic reticulum turnover during stress recovery. Nat Cell Biol 18, 1173–1184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

