Incorporating the social context into neurocognitive models of adolescent decision-making: A neuroimaging meta-analysis
- PMID: 31006540
- PMCID: PMC6659412
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.12.024
Incorporating the social context into neurocognitive models of adolescent decision-making: A neuroimaging meta-analysis
Abstract
Neurobiological models of adolescent decision-making emphasize developmental changes in brain regions involved in affect (e.g., ventral striatum) and cognitive control (e.g., lateral prefrontal cortex). Although social context plays an important role in adolescent decision-making, current models do not discuss brain regions implicated in processing social information (e.g., dorsomedial prefrontal cortex). We conducted a coordinate-based meta-analysis using the Multilevel peak Kernel Density Analysis (MKDA) method to test the hypothesis that brain regions involved in affect, cognitive control, and social information processing support adolescent decision-making in social contexts (N = 21 functional neuroimaging studies; N = 1292 participants). Results indicated that dorsomedial prefrontal cortex, inferior frontal gyrus/insula and ventral striatum are consistently associated with adolescent decision-making in social contexts. Activity within these regions was modulated by the type of social context and social actors involved. Findings suggest including brain regions involved in social information processing into models of adolescent decision-making. We propose a 'constructionist' model, which describes psychological processes and corresponding neural networks related to affect, cognitive control, and social information processing.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
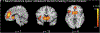
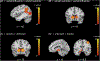
Similar articles
-
Differential effects of parent and peer presence on neural correlates of risk taking in adolescence.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2018 Sep 11;13(9):945-955. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsy071. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30137631 Free PMC article.
-
Peers influence adolescent reward processing, but not response inhibition.Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2018 Apr;18(2):284-295. doi: 10.3758/s13415-018-0569-5. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29470796
-
Adolescent risky decision-making: neurocognitive development of reward and control regions.Neuroimage. 2010 May 15;51(1):345-55. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.02.038. Epub 2010 Feb 24. Neuroimage. 2010. PMID: 20188198
-
The differential neural substrates for reward choice under gain-loss contexts and risk in alcohol use disorder: Evidence from a voxel-based meta-analysis.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2023 Jul 1;248:109912. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2023.109912. Epub 2023 May 4. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2023. PMID: 37182355 Review.
-
The involvement of the striatum in decision making.Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2016 Mar;18(1):55-63. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2016.18.1/sfecteau. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27069380 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Apples to apples? Neural correlates of emotion regulation differences between high- and low-risk adolescents.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2019 Aug 31;14(8):827-836. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsz063. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31506678 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic connectivity within the affective salience network moderates adolescent susceptibility to negative and positive peer norms.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 19;12(1):17463. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17780-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36261429 Free PMC article.
-
Age and Gender Effects in Sensitivity to Social Rewards in Adolescents and Young Adults.Front Behav Neurosci. 2019 Jul 29;13:171. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2019.00171. eCollection 2019. Front Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31417377 Free PMC article.
-
A Domain-General Developmental "Do-GooD" Network Model of Prosocial Cognition in Adolescence: A Systematic Review.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Mar 8;16:815811. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.815811. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35350389 Free PMC article.
-
Neural Dynamic Responses of Monetary and Social Reward Processes in Adolescents.Front Hum Neurosci. 2020 Apr 21;14:141. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2020.00141. eCollection 2020. Front Hum Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32372935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aztil S, Parrish MJ, Satpute A, Shablack H, Brooks JA, & Lindquist KA (in preparation). A social dimension of the evaluative brain
-
- Barrett LF (2017). How emotions are made: The secret life of the brain Houghton Mifflin Harcourt.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

