Inhibitory effects of rubratoxin A, a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2, on the Ca2+-dependent contraction of skinned carotid artery from guinea pig
- PMID: 31006724
- PMCID: PMC6473161
- DOI: 10.1540/jsmr.55.14
Inhibitory effects of rubratoxin A, a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2, on the Ca2+-dependent contraction of skinned carotid artery from guinea pig
Abstract
Rubratoxin A, a potent inhibitor of PP2A, is known to suppress smooth muscle contraction. The inhibitory role of PP2A in smooth muscle contraction is still unclear. In order to clarify the regulatory mechanisms of PP2A on vascular smooth muscle contractility, we examined the effects of rubratoxin A on the Ca2+-induced contraction of β-escin skinned carotid artery preparations from guinea pigs. Rubratoxin A at 1 µM and 10 µM significantly inhibited skinned carotid artery contraction at any Ca2+ concentration. The data fitting to the Hill equation in [Ca2+]-contraction relationship indicated that rubratoxin A decreased Fmax-Ca2+ and increased [Ca2+]50, indices of Ca2+ sensitivity for the force and myosin-actin interaction, respectively. These results suggest that PP2A inhibition causes downregulation of the myosin light chain phosphorylation and direct interference with myosin-actin interaction.
Keywords: Ca2+ sensitivity; contractile proteins; protein phosphatase 2A; rubratoxin A; vascular smooth muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
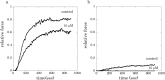
 ), 10 nM (
), 10 nM ( ), 100 nM (
), 100 nM ( ), 1 µM (
), 1 µM ( ), or 10 µM (
), or 10 µM ( ) rubratoxin
A was added to the artificial intracellular solutions. Values are the means ± S.E.M.
of 4–7 experiments. Asterisk indicates significant difference of the active force
compared with that of controls, where P values are less than
0.05.
) rubratoxin
A was added to the artificial intracellular solutions. Values are the means ± S.E.M.
of 4–7 experiments. Asterisk indicates significant difference of the active force
compared with that of controls, where P values are less than
0.05.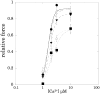
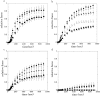
 ), 10 nM (
), 10 nM ( ), 100 nM (
), 100 nM ( ), 1 µM
(
), 1 µM
( ), or 10
µM (
), or 10
µM ( ) rubratoxin A was added to the artificial intracellular solutions.
) rubratoxin A was added to the artificial intracellular solutions.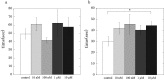
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of contraction and myosin light chain phosphorylation in guinea-pig smooth muscle by p21-activated kinase 1.J Physiol. 2003 Jun 1;549(Pt 2):489-500. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.033167. Epub 2003 Apr 11. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12692179 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of an expected actin-tropomyosin binding region of heat shock protein 20 on the relaxation in skinned carotid artery and taenia cecum from guinea pig.J Smooth Muscle Res. 2009 Feb;45(1):63-74. doi: 10.1540/jsmr.45.63. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2009. PMID: 19377274
-
Effects of calyculin A on tension and myosin phosphorylation in skinned smooth muscle of the rabbit mesenteric artery.Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):703-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13631.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1993. PMID: 8395295 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the Ca(2+)-sensitivity in phasic and tonic smooth muscle.Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 1992;54(3):217-51. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 1992. PMID: 1413985 Review.
-
The Ayerst Award Lecture 1990. Calcium-dependent mechanisms of regulation of smooth muscle contraction.Biochem Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;69(12):771-800. doi: 10.1139/o91-119. Biochem Cell Biol. 1991. PMID: 1818584 Review.
References
-
- Gong MC, Cohen P, Kitazawa T, Ikebe M, Masuo M, Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV. Myosin light chain phosphatase activities and the effects of phosphatase inhibitors in tonic and phasic smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1992; 267(21): 14662–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

