Intralesional Injection of Botulinum Toxin Type A Compared with Intralesional Injection of Corticosteroid for the Treatment of Hypertrophic Scar and Keloid: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 31006769
- PMCID: PMC6489528
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.916305
Intralesional Injection of Botulinum Toxin Type A Compared with Intralesional Injection of Corticosteroid for the Treatment of Hypertrophic Scar and Keloid: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
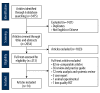
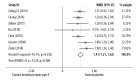
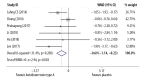
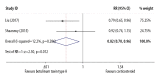
BACKGROUND The optimal treatment for hypertrophic scar and keloid remains controversial. Therefore, the aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to compare the effectiveness of intralesional injection of botulinum toxin type A compared with placebo and intralesional injection of corticosteroid compared with placebo in patients with hypertrophic scar and keloid. MATERIAL AND METHODS Six databases were searched using Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) keywords and included Web of Science, PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library, WanFang, and CNKI from their inception to March 1 2019, without language restriction. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and prospective controlled trials (PCTs) were identified that compared intralesional injection of botulinum toxin type A with placebo and corticosteroid with placebo in hypertrophic scar and keloid. The quality of controlled trials was assessed by the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS). RESULTS Comparison of intralesional botulinum toxin type A and corticosteroid showed significant differences in the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) (P<0.001) (WMD, -4.30; 95% CI, -4.44 to -4.16) and effective rate (P=0.012) (RR=0.82; 95% CI, 0.70-0.96). Intralesional injection of botulinum toxin type A compared with placebo showed significant differences in the VAS (P<0.001) (WMD, 1.41; 95% CI, 1.21-1.62), the width of scar (P=0.00) (WMD, -0.15; 95% CI, -0.19 to -0.10) and Vancouver Scar Scale (VSS) (P=0.003) (WMD, -0.69; 95% CI, -1.14 to -0.23). CONCLUSIONS Systematic review and meta-analysis showed that injection of intralesional botulinum toxin type A was more effective in the treatment of hypertrophic scar and keloid than injection of intralesional corticosteroid or placebo.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
-
- Nast A, Eming S, Fluhr J, et al. German S2k guidelines for the therapy of pathological scars (hypertrophic scars and keloids) J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2012;10(10):747–62. - PubMed
-
- Ogawa R. The most current algorithms for the treatment and prevention of hypertrophic scars and keloids. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;125:557–68. - PubMed
-
- Wolfram D, Tzankov A, Pülzl P, Piza-Katzer H. Hypertrophic scars and keloids – a review of their pathophysiology, risk factors, and therapeutic management. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35:171–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

