Multispecies study: low-dose tributyltin impairs ovarian theca cell cholesterol homeostasis through the RXR pathway in five mammalian species including humans
- PMID: 31006824
- PMCID: PMC6625865
- DOI: 10.1007/s00204-019-02449-y
Multispecies study: low-dose tributyltin impairs ovarian theca cell cholesterol homeostasis through the RXR pathway in five mammalian species including humans
Abstract
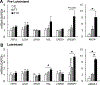
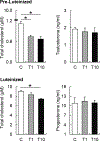
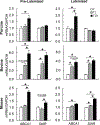
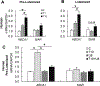
Tributyltin (TBT), an organotin chemical used as a catalyst and biocide, can stimulate cholesterol efflux in non-steroidogenic cells. Since cholesterol is the first limiting step for sex hormone production, we hypothesized that TBT disrupts intracellular cholesterol transport and impairs steroidogenesis in ovarian theca cells. We investigated TBT's effect on cholesterol trafficking, luteinization, and steroidogenesis in theca cells of five species (human, sheep, cow, pig, and mice). Primary theca cells were exposed to an environmentally relevant dose of TBT (1 or 10 ng/ml) and/or retinoid X receptor (RXR) antagonist. The expression of RXRα in sheep theca cells was knocked down using shRNA. Steroidogenic enzymes, cholesterol transport factors, and nuclear receptors were measured by RT-qPCR and Western blotting, and intracellular cholesterol, progesterone, and testosterone secretion by ELISA. TBT upregulated StAR and ABCA1 in ovine cells, and SREBF1 mRNA in theca cells. TBT also reduced intracellular cholesterol and upregulated ABCA1 protein expression but did not alter testosterone or progesterone production. RXR antagonist and RXRα knockdown demonstrates that TBT's effect is partially through RXR. TBT's effect on ABCA1 and StAR expression was recapitulated in all five species. TBT, at an environmentally relevant dose, stimulates theca cell cholesterol extracellular efflux via the RXR pathway, triggers a compensatory upregulation of StAR that regulates cholesterol transfer into the mitochondria and SREBF1 for de novo cholesterol synthesis. Similar results were obtained in all five species evaluated (human, sheep, cow, pig, and mice) and are supportive of TBT's conserved mechanism of action across mammalian species.
Keywords: Cholesterol; Luteinization; Retinoid X receptor; Steroidogenesis; Theca cells; Tributyltin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
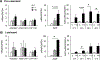
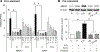

Similar articles
-
The organotin triphenyltin disrupts cholesterol signaling in mammalian ovarian steroidogenic cells through a combination of LXR and RXR modulation.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 15;453:116209. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2022.116209. Epub 2022 Aug 23. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35998708 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Lipids and Lipid-Related Transcripts in Human and Ovine Theca Cells and an in Vitro Mouse Model Exposed to the Obesogen Chemical Tributyltin.Environ Health Perspect. 2024 Apr;132(4):47009. doi: 10.1289/EHP13955. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Environ Health Perspect. 2024. PMID: 38630605 Free PMC article.
-
The obesogen tributyltin induces abnormal ovarian adipogenesis in adult female rats.Toxicol Lett. 2018 Oct 1;295:99-114. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.06.1068. Epub 2018 Jun 15. Toxicol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29908848
-
Lipoprotein enhancement of ovarian theca-interstitial cell steroidogenesis: relative contribution of scavenger receptor class B (type I) and adenosine 5'-triphosphate- binding cassette (type A1) transporter in high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol transport and androgen synthesis.Endocrinology. 2003 Jun;144(6):2437-45. doi: 10.1210/en.2002-221110. Endocrinology. 2003. PMID: 12746305
-
Tributyltin: Advancing the Science on Assessing Endocrine Disruption with an Unconventional Endocrine-Disrupting Compound.Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2018;245:65-127. doi: 10.1007/398_2017_8. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29119384 Review.
Cited by
-
A 3-dimensional microfluidic platform for modeling human extravillous trophoblast invasion and toxicological screening.Lab Chip. 2021 Feb 9;21(3):546-557. doi: 10.1039/d0lc01013h. Lab Chip. 2021. PMID: 33166377 Free PMC article.
-
Bisphenol S and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Signaling in Human Placental Cytotrophoblasts.Environ Health Perspect. 2021 Feb;129(2):27005. doi: 10.1289/EHP7297. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Environ Health Perspect. 2021. PMID: 33605785 Free PMC article.
-
Bisphenol S enhances gap junction intercellular communication in ovarian theca cells.Chemosphere. 2021 Jan;263:128304. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128304. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Chemosphere. 2021. PMID: 33155548 Free PMC article.
-
Organotin Antifouling Compounds and Sex-Steroid Nuclear Receptor Perturbation: Some Structural Insights.Toxics. 2022 Dec 27;11(1):25. doi: 10.3390/toxics11010025. Toxics. 2022. PMID: 36668751 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced bioenergetics and mitochondrial fragmentation in human primary cytotrophoblasts induced by an EGFR-targeting chemical mixture.Chemosphere. 2024 Sep;364:143301. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2024.143301. Epub 2024 Sep 7. Chemosphere. 2024. PMID: 39251161
References
-
- Agency USEP (1997) Toxicological Review Tributyltin Oxide. Washington D.C.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

