Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) phosphorylation is a key regulator of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS) cell viability and migration
- PMID: 31006845
- PMCID: PMC11810355
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-019-02913-3
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) phosphorylation is a key regulator of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS) cell viability and migration
Abstract
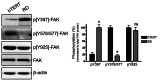
Background: Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is the most common soft-tissue sarcoma in children. Pathogenesis of RMS is associated with aggressive growth pattern and increased risk of morbidity and mortality. There are two main subtypes or RMS: embryonal and alveolar. The embryonal type is characterized by distinct molecular aberrations, including alterations in the activity of certain protein kinases. Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase that plays a vital role in focal adhesion (FA) assembly to promote cytoskeleton dynamics and regulation of cell motility. It is regulated by multiple phosphorylation sites: tyrosine 397, Tyr 576/577, and Tyr 925. Tyrosine 397 is the autophosphorylation site that regulates FAK localization at the cell periphery to facilitate the assembly and formation of the FA complex. The kinase activity of FAK is mediated by the phosphorylation of Tyr 576/577 within the kinase domain activation loop. Aberrations of FAK phosphorylation have been linked to the pathogenesis of different types of cancers. In this regard, pY397 upregulation is linked to increase ERMS cell motility, invasion, and tumorigenesis.
Methods: In this study, we have used an established human embryonal muscle rhabdomyosarcoma cell line RD as a model to examine FAK phosphorylation profiles to characterize its role in the pathogenies of RMS.
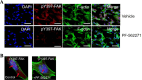
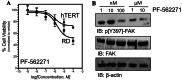
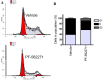
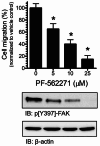
Results: Our findings revealed a significant increase of FAK phosphorylation at pY397 in RD cells compared to control cells (hTERT). On the other hand, Tyr 576/577 phosphorylation levels in RD cells displayed a pronounced reduction. Our data showed that Y925 residue exhibited no detectable change. The in vitro analysis showed that the FAK inhibitor, PF-562271 led to G1 cell-cycle arrest induced cell death (IC50, ~ 12 µM) compared to controls. Importantly, immunostaining analyses displayed a noticeable reduction of Y397 phosphorylation following PF-562271 treatment. Our data also showed that PF-562271 suppressed RD cell migration in a dose-dependent manner associated with a reduction in Y397 phosphorylation.
Conclusions: The data presented herein indicate that targeting FAK phosphorylation at distinct sites is a promising strategy in future treatment approaches for defined subgroups of rhabdomyosarcoma.
Keywords: Cell migration; Focal adhesion kinase (FAK); Phosphorylation; Rhabdomyosarcoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Focal adhesion kinase promotes ribosome biogenesis to drive advanced thyroid cancer cell growth and survival.Front Oncol. 2025 May 19;15:1252544. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1252544. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40458728 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro effects and ex vivo binding of an EGFR-specific immunotoxin on rhabdomyosarcoma cells.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015 Jun;141(6):1049-61. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1884-z. Epub 2014 Nov 30. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25433506 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Focal Adhesion Kinase and Vinculin Expression on Migration Parameters of Normal and Tumor Epitheliocytes.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2024 Mar;89(3):474-486. doi: 10.1134/S0006297924030088. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2024. PMID: 38648767
-
Levetiracetam add-on for drug-resistant focal epilepsy: an updated Cochrane Review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;2012(9):CD001901. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001901.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22972056 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on Cell Growth and Migration of A549 Cells under Simulated Microgravity.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 May 31;12(11):1879. doi: 10.3390/nano12111879. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35683734 Free PMC article.
-
Artesunate alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial necrosis in rats and hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in H9C2 cells via regulating the FAK/PI3K/Akt pathway.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Oct;8(20):1291. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-5182. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 33209871 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights on the Nuclear Functions and Targeting of FAK in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 11;23(4):1998. doi: 10.3390/ijms23041998. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breast Cancer Prognosis Prediction and Immune Pathway Molecular Analysis Based on Mitochondria-Related Genes.Genet Res (Camb). 2022 May 31;2022:2249909. doi: 10.1155/2022/2249909. eCollection 2022. Genet Res (Camb). 2022. PMID: 35707265 Free PMC article.
-
Focal adhesion kinase inhibitors, a heavy punch to cancer.Discov Oncol. 2021 Nov 22;12(1):52. doi: 10.1007/s12672-021-00449-y. Discov Oncol. 2021. PMID: 35201485 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beierle EA et al (2008) Focal adhesion kinase expression in human neuroblastoma: immunohistochemical and real-time PCR analyses. Clin Cancer Res 14(11):3299–3305 - PubMed
-
- Canel M et al (2006) Overexpression of focal adhesion kinase in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is independent of fak gene copy number. Clin Cancer Res 12(11 Pt 1):3272–3279 - PubMed
-
- Cen L et al (2007) Phosphorylation profiles of protein kinases in alveolar and embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Mod Pathol 20(9):936–946 - PubMed
-
- Cohen LA, Guan JL (2005) Mechanisms of focal adhesion kinase regulation. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 5(8):629–643 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

