Free-breathing cine imaging with motion-corrected reconstruction at 3T using SPiral Acquisition with Respiratory correction and Cardiac Self-gating (SPARCS)
- PMID: 31006916
- PMCID: PMC6510595
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.27763
Free-breathing cine imaging with motion-corrected reconstruction at 3T using SPiral Acquisition with Respiratory correction and Cardiac Self-gating (SPARCS)
Abstract
Purpose: To develop a continuous-acquisition cardiac self-gated spiral pulse sequence and a respiratory motion-compensated reconstruction strategy for free-breathing cine imaging.
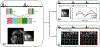
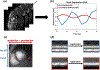
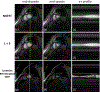
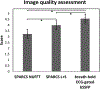
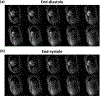
Methods: Cine data were acquired continuously on a 3T scanner for 8 seconds per slice without ECG gating or breath-holding, using a golden-angle gradient echo spiral pulse sequence. Cardiac motion information was extracted by applying principal component analysis on the gridded 8 × 8 k-space center data. Respiratory motion was corrected by rigid registration on each heartbeat. Images were reconstructed using a low-rank and sparse (L+S) technique. This strategy was evaluated in 37 healthy subjects and 8 subjects undergoing clinical cardiac MR studies. Image quality was scored (1-5 scale) in a blinded fashion by 2 experienced cardiologists. In 13 subjects with whole-heart coverage, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) from SPiral Acquisition with Respiratory correction and Cardiac Self-gating (SPARCS) was compared to that from a standard ECG-gated breath-hold balanced steady-state free precession (bSSFP) cine sequence.
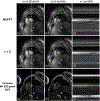
Results: The self-gated signal was successfully extracted in all cases and demonstrated close agreement with the acquired ECG signal (mean bias, -0.22 ms). The mean image score across all subjects was 4.0 for reconstruction using the L+S model. There was good agreement between the LVEF derived from SPARCS and the gold-standard bSSFP technique.
Conclusion: SPARCS successfully images cardiac function without the need for ECG gating or breath-holding. With an 8-second data acquisition per slice, whole-heart cine images with clinically acceptable spatial and temporal resolution and image quality can be acquired in <90 seconds of free-breathing acquisition.
Keywords: cardiac MRI; golden angle; low-rank and sparse; motion correction; self-gating; spiral trajectory.
© 2019 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures

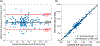


References
-
- Shetty AN. Suppression of Radiofrequency Interference in Cardiac Gated MRI: A Simple Design. Magn. Reson. Med 1988;8:84–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

